FLAC3D Theory and Background • Constitutive Models
Comparison of Plastic-Hardening Model without and with Small-Strain Stiffness
Note
To view this project in FLAC3D, use the menu command . The project’s main data files are shown at the end of this example.
This example compares the behavior of the Plastic-Hardening (PH) model without and with small-strain stiffness during triaxial compression. Both models comprise a one-zone triaxial compression test with a constant cell pressure of 100 kPa. Case 1 is the standard PH model without small-strain stiffness, and Case 2 is the PH model with small-strain stiffness. The parameters are listed in Table 1.
Basic Parameters: |
|
\(\phi\) (degrees) |
30 |
\(c\) (kPa) |
0 |
\(\psi\) (degrees) |
10 |
\(E^{ref}_{50}\) (kPa) |
3e4 |
\(E^{ref}_{ur}\) (kPa) |
8e4 |
\(\nu\) |
0.25 |
\(m\) |
0.55 |
\(p^{ref}\) (kPa) |
100 |
Small-Strain Parameters: |
|
\(E^{ref}_{0}\) (kPa) |
3e5 |
\(\gamma_{70}\) (default) |
2e-4 |
Figure 1 plots deviatoric stress versus axial strain for both cases. Both cases generally have the same backbone loading path. The difference is the unloading and reloading paths. In Case 1, the reloading path is exactly the reverse of the unloading path. However, in Case 2, the unloading and reloading paths are district and the apparent hysteretic loops are observed.
Figure 2 shows the elastic shear moduli for both cases. In Case 1, the elastic shear modulus keep constant with a value of \(G_{ur}\), but in Case 2 the elastic shear modulus decreases from the initial value of \(G_{0}\) to the value of \(G_{ur}\), and then keep the value of value of \(G_{ur}\) as expected.
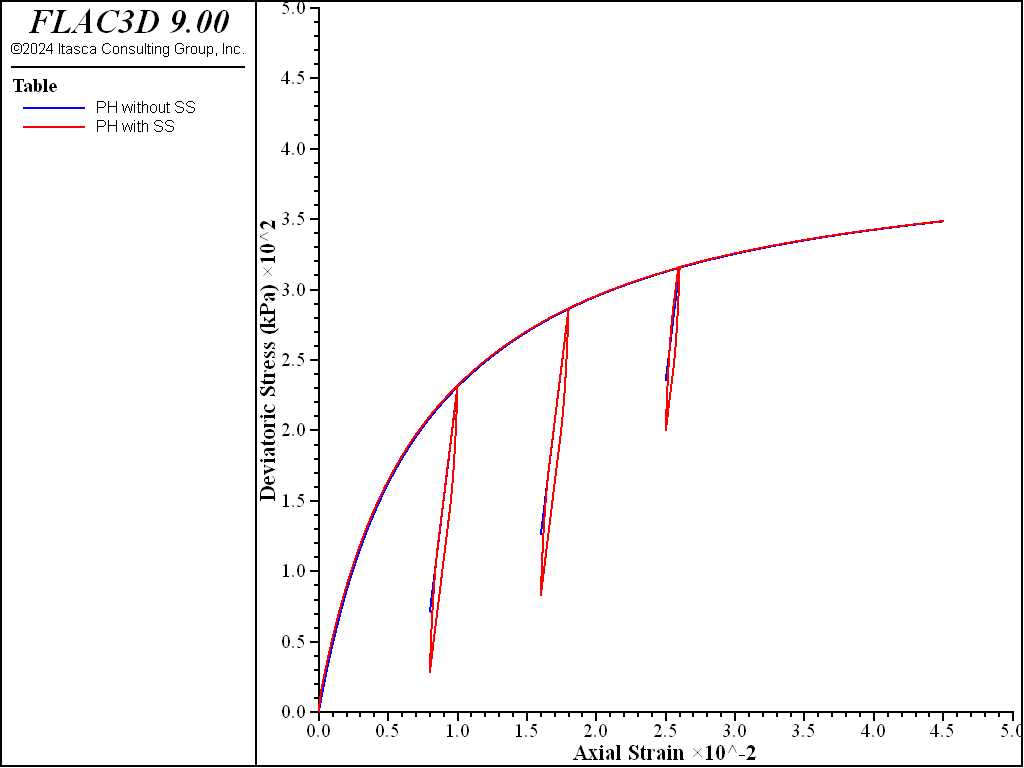
Figure 1: Comparison of deviatoric stresses without and with small-strain stiffness.
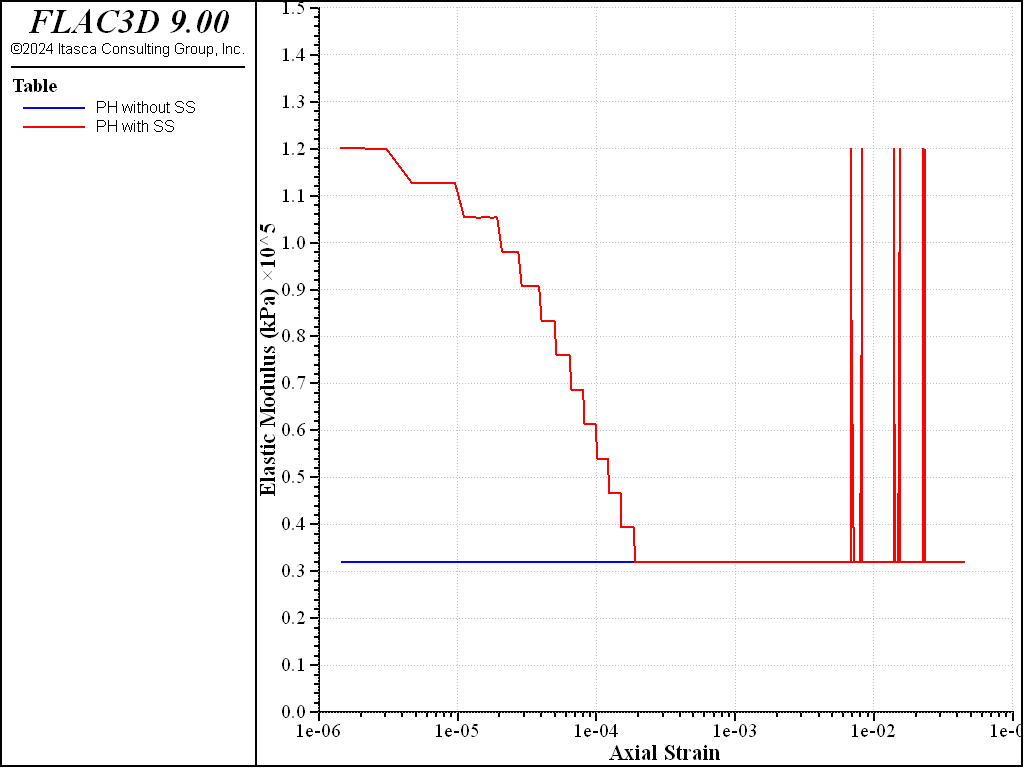
Figure 2: Comparison of elastic moduli without and with small-strain stiffness.
Data Files
TriaxialCompressionSmallStrainPlasticHardening.dat
model new
model large-strain off
model configure axisymmetry
;
zone create quadrilateral size 1 1
zone cmodel assign plastic-hardening
zone property stiffness-50-reference=3.0e4 stiffness-ur-reference=8.0e4
zone property pressure-reference=100.0 exponent=0.55 poisson=0.25
zone property coefficient-normally-consolidation=0.40
zone property friction=40.0 dilation=10.0 cohesion=0.0
zone property stress-1-effective=-100.0 stress-2-effective=-100.0 ...
stress-3-effective=-100.0
zone property flag-smallstrain=true stiffness-0-reference=30.0e4 ...
strain-70=2e-4
;
zone gridpoint fix velocity-y
zone face apply stress-xx=-100.0 range position-x 1
zone initialize stress xx -100.0 yy -100.0 zz -100.0
;
[global zp_ = zone.head]
[global gp_ = gp.find(4)]
fish define hhhq_
global hhhq_ = zone.stress.xx(zp_) - zone.stress.yy(zp_)
global hhha_ = -gp.disp.y(gp_)
global G_ = zone.prop(zp_,'shear')
global strain_ = zone.strain.shear.inc(zp_)
end
history interval 5
fish history hhhq_
fish history hhha_
fish history G_
fish history strain_
;
zone gridpoint initialize velocity-y -4e-7 range position-y 1
model step 25000
zone gridpoint initialize velocity-y 4e-7 range position-y 1
model step 5000
zone gridpoint initialize velocity-y -4e-7 range position-y 1
model step 25000
zone gridpoint initialize velocity-y 4e-7 range position-y 1
model step 5000
zone gridpoint initialize velocity-y -4e-7 range position-y 1
model step 25000
zone gridpoint initialize velocity-y 2e-7 range position-y 1
model step 5000
zone gridpoint initialize velocity-y -4e-7 range position-y 1
model step 50000
;
history export '1' vs '2' table 'phs_qs_100'
table 'phs_qs_100' export 'phs_qs_100' truncate
history export '3' vs '4' table 'phs_Gs_100'
table 'phs_Gs_100' export 'phs_Gs_100' truncate
;
model save 'phs_w100'
| Was this helpful? ... | Itasca Software © 2024, Itasca | Updated: Nov 12, 2025 |
