Maxwell Model: Oedometer Test
Note
To view this project in 3DEC, use the menu command . The project’s main data files are shown at the end of this example.
This example compares numerical and analytical solutions of an oedometer test carried out on a Maxwell substance. In this test, the base of the sample is fixed, lateral deformations are prevented, and a constant vertical load, \(P\), is applied at the top of the specimen.
The analytical solution for vertical strain and stresses is
where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the three constants:
\(K\) and \(G\) are bulk and shear modulus of the substance, and \(\eta\) is the viscosity.
The numerical simulation is carried out simultaneously on three samples, represented by one zone, using the Maxwell model, the Burgers model and the Burgers-Mohr model.
Because no value is assigned to the property viscosity-kelvin for the Burgers model and the Maxwell-Mohr model, the Kelvin cell logic is not taken into account by the models. Also, the cohesion property is set to a high value to prevent triggering of the plasticity logic for the Burgers-Mohr model. The initial state is obtained by cycling the model to elastic equilibrium. For the viscous response, velocities are reset to zero, and the initial timestep is set to a small value (\(\Delta t\) = 10-6) compared to the ratio of viscosity over shear modulus (\(\eta ^M/G^M\) = 2.0). With the choice of default automatic creep timestep parameter settings used in the example, the timestep increases by a factor of 1.01 when the out-of-balance force ratio is less than 10-3, until \(\Delta t\) = 10-2. A state of hydrostatic stress is reached at the end of the test. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the agreement between analytical solutions and numerical predictions for stresses and strains in the three samples.
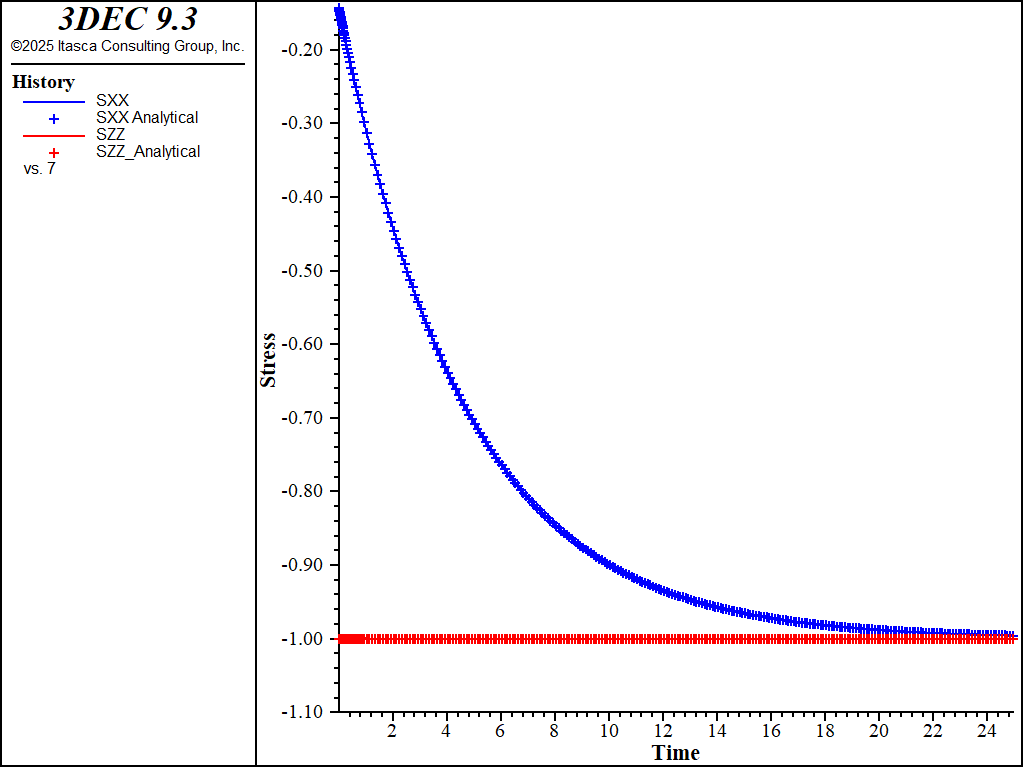
Figure 1: Oedometer test on a Maxwell substance: analytical and numerical stress values versus time.
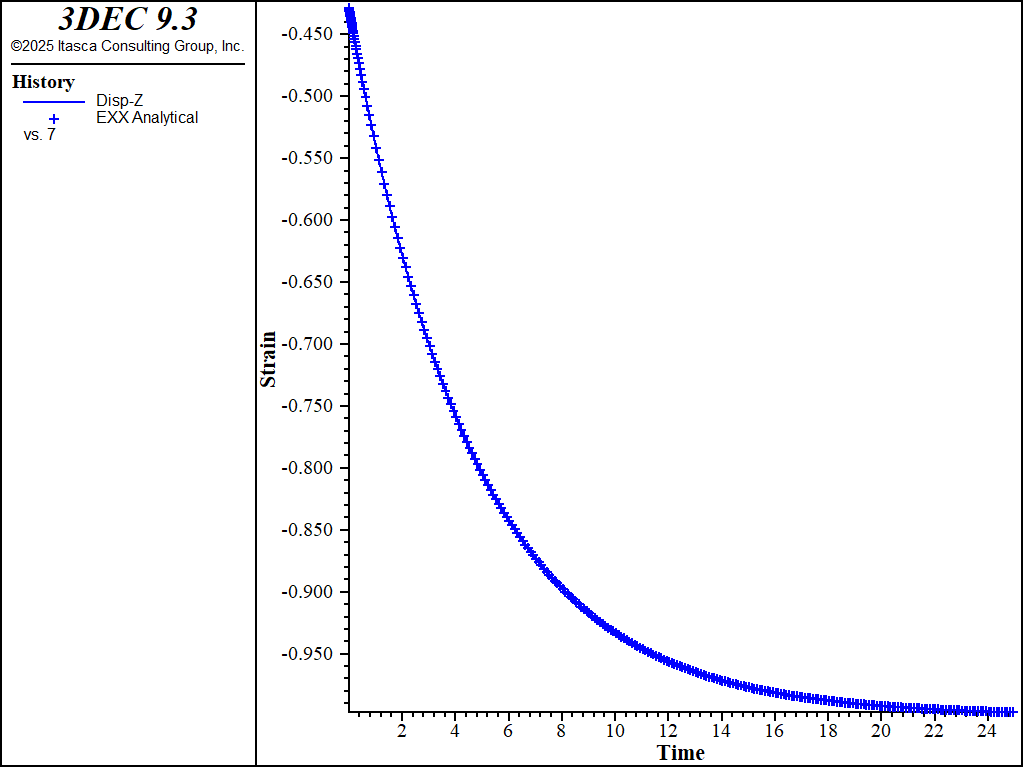
Figure 2: Oedometer test on a Maxwell substance: analytical and numerical strain values versus time.
Data Files
OedometerMaxwell.dat
;------------------------------------------------------------
; Oedometer test -- Maxwell substance
;-------------------------------------------------------------------
model new
fish automatic-create off
model title "Oedometer test --- 'Maxwell' substance"
model configure creep
model large-strain off
fish define ini_cons
global c_bu = 1.
global c_sh = 1.
global c_vi = 2.
global c_pr = -1.
local a1 = c_bu + 4. * c_sh / 3.
global c_a = 2. * c_sh / a1
global c_b = c_a * c_bu / (2. * c_vi)
global c_c = c_a * 2. / 3.
global c_d = -c_pr / c_bu
end
[ini_cons]
; --- model ---
block create brick 0 1
block zone generate edgelength 1.0
block zone cmodel assign burgers-mohr
block zone property density 1 bulk [c_bu] shear-maxwell [c_sh] cohesion 1E20
block zone property tension 1E20 viscosity-maxwell [c_vi]
block face apply stress 0.0 0.0 [c_pr] 0 0 0 range position-z 1
block gridpoint apply velocity-x 0 range position-x 0 1
block gridpoint apply velocity-y 0 range position-y 0 1
block gridpoint apply velocity-z 0 range position-z 0
; --- elastic equilibrium ---
model solve
; --- histories ---
program call 'analytical.fis'
fish history name 'SXX' sxx
fish history name 'SXX Analytical' ana_sxx
fish history name 'SZZ' szz
fish history name 'SZZ_Analytical' ana_szz
block history name 'Disp-Z' displacement-z position 0.0 0.0 1.0
fish history name 'EXX Analytical' ana_ezz
model history creep time-total
model history timestep
; --- reset velocities to zero ---
block gridpoint initialize velocity (0,0,0)
; --- viscous behaviour ---
model creep timestep starting 1.e-6
model creep timestep minimum 1.e-6
model creep timestep maximum 1.e-2
model solve time-total=25.
model save 'maxwell'
program return
| Was this helpful? ... | Itasca Software © 2024, Itasca | Updated: May 15, 2025 |
