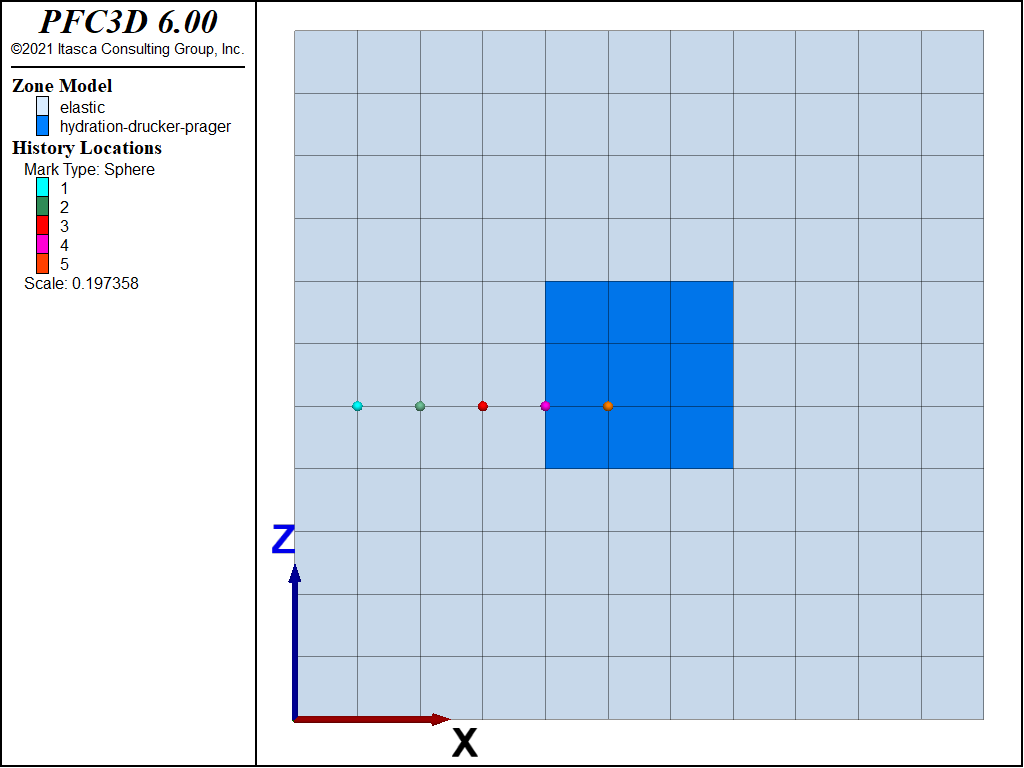
Concrete Inclusion in an Elastic Medium
Note
To view this project in FLAC3D, use the menu command . Choose “Thermal/ConcreteInclusion” and select “ConcreteInclusion.f3dprj” to load. The project’s main data files are shown at the end of this example.
This example consists of a concrete inclusion inside an elastic and thermal isotropic material. The model has a size of 10 m × 1 m × 10 m and is fixed in the y-direction (Figure 1). Roller boundary conditions are applied at the model boundaries. The material properties are listed in Table 1 (elastic frame) and Table 2 (concrete inclusion). The model was run for a thermal time of two days.
Figure 2 to Figure 6 show the evolution of various parameters during the hydration process: gridpoint temperatures at five points (Figure 2); hydration grade (Figure 3); tensile and compressive strength (Figure 4); elastic parameters (Figure 5); and the generated hydration heat (Figure 6).
| Bulk modulus (\(K\)) | 1000 MPa |
| Shear modulus (\(G\)) | 700 MPa |
| Specific heat (\(C_p\)) | 0.2 J/kg/K |
| Thermal conductivity (\(k\)) | 20.0 W/m/K |
| Linear thermal expansion coefficient (\(\alpha_t\)) | 10-4 K-1 |
| Maximum amount of generated heat (\(Q^{max}_{Ce}\)) | 105 J/kg |
| Cement concentration (\(C\)) | 330 kg/m3 |
| Material parameter (\(b\)) | -1.114 |
| Material parameter (\(t_1\)) | 7.2 \(\cdot\) 104 [s] |
| Universal gas constant (\(R\)) | 8.314 J/mol |
| Activation energy (\(E_{A,1}\)) | 33.5 J/mol |
| Slope of energy change (\(dE_{A,T}\)) | 1.47 J/mol/K |
| Specific heat (\(C_{P,1}\)) | 0.2 J/kg/K |
| Thermal conductivity (\(\lambda_1\)) | 2.0 W/m/K |
| Linear thermal expansion coefficient (\(\alpha_t\)) | 10-5 K-1 |
| Specific parameter for cement (\(\alpha_0\)) | 0.20 |
| Young’s modulus after complete hydration (\(E_{cte}\)) | 1000 MPa |
| Material parameter (\(c\)) | 0.4 |
| Material parameter (\(a\)) | 0.6 |
| Minimum value for (\(\alpha - \alpha_0\)) | 10-4 |
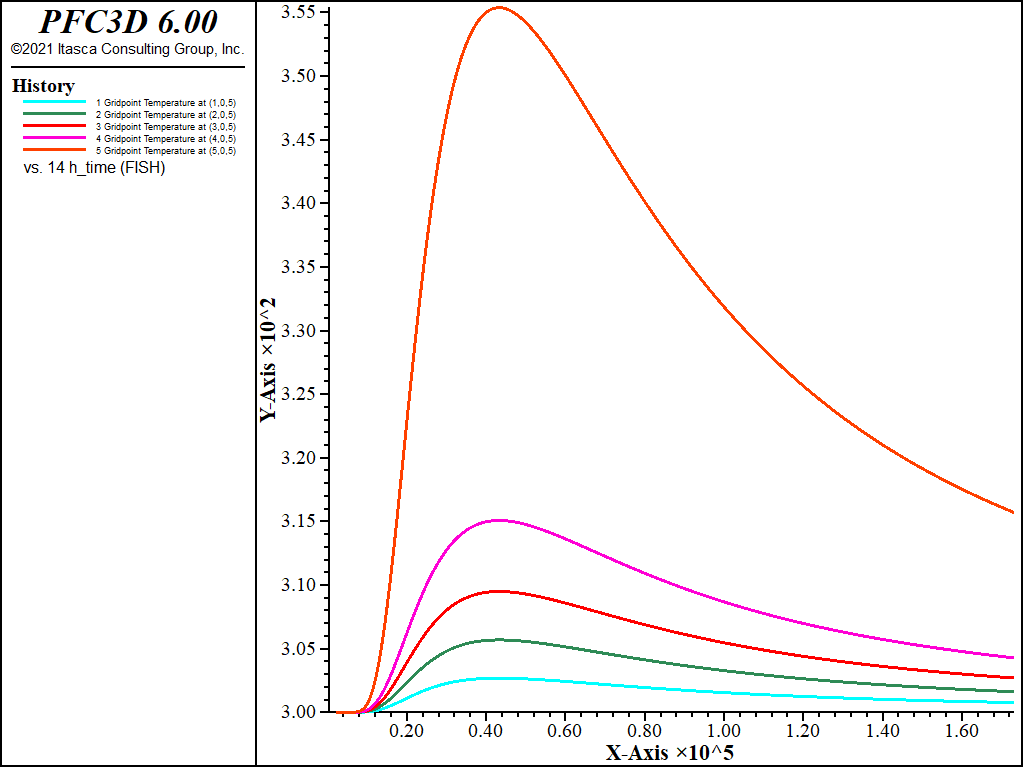
Figure 2: Evolution of gridpoint temperatures for the concrete inclusion test as a function of the concrete age.
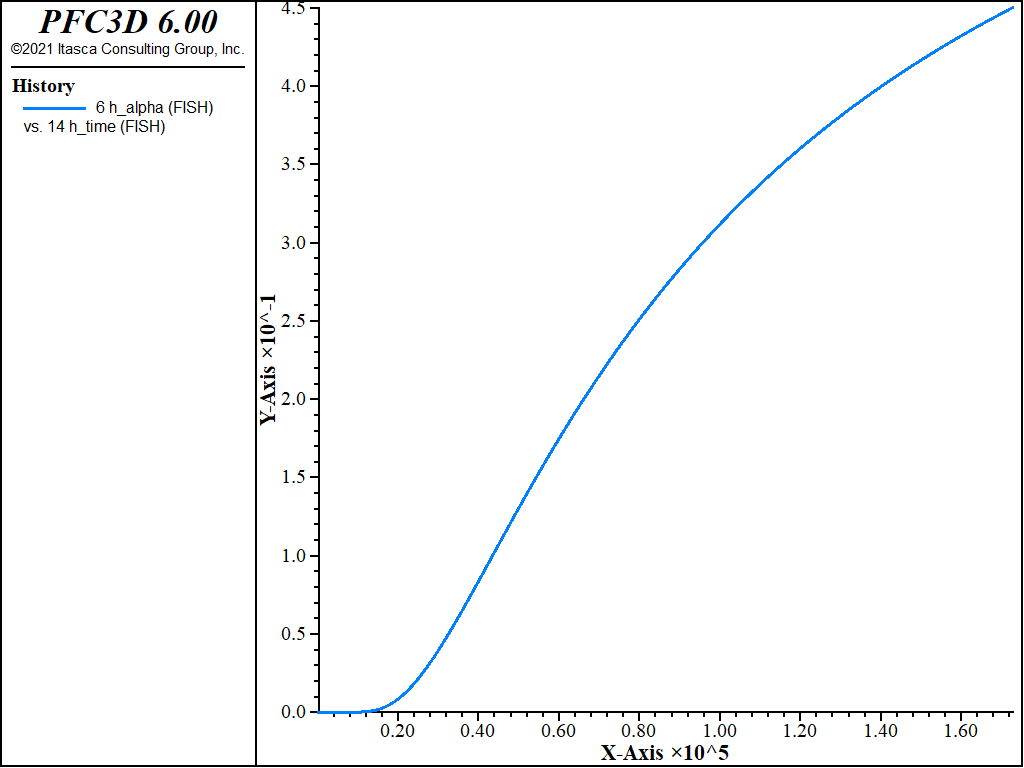
Figure 3: Evolution of the hydration grade for the center zone of the concrete inclusion as a function of the concrete age.
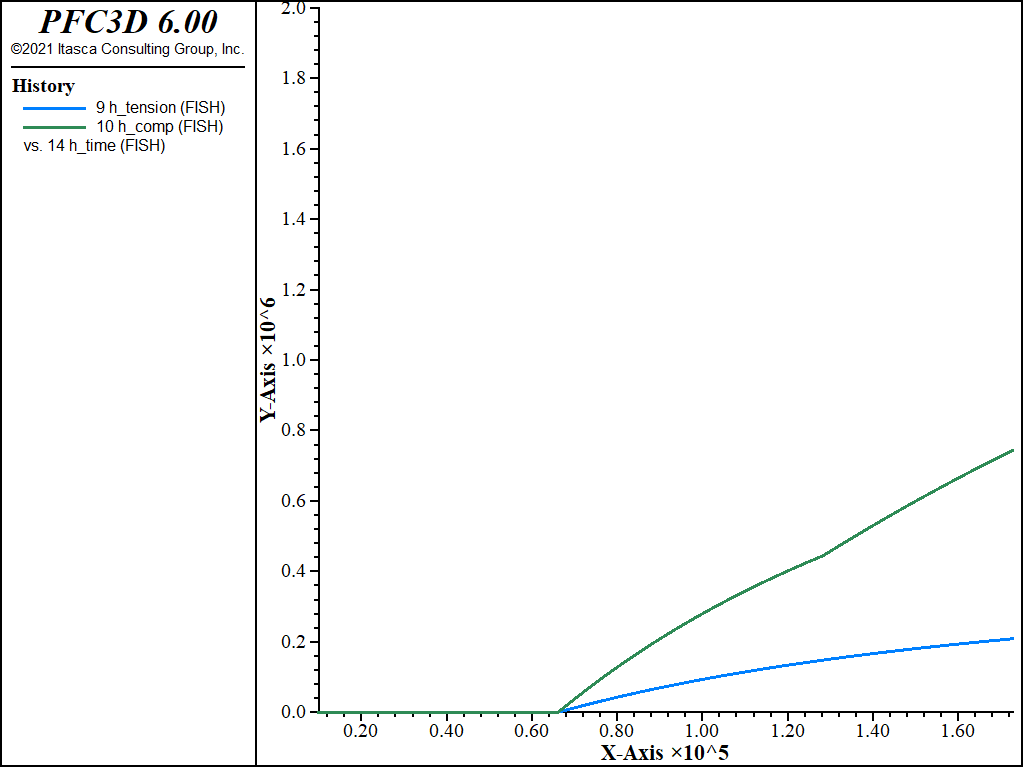
Figure 4: Evolution of the tensile and compressive strength for the center zone of the concrete inclusion as a function of the concrete age.
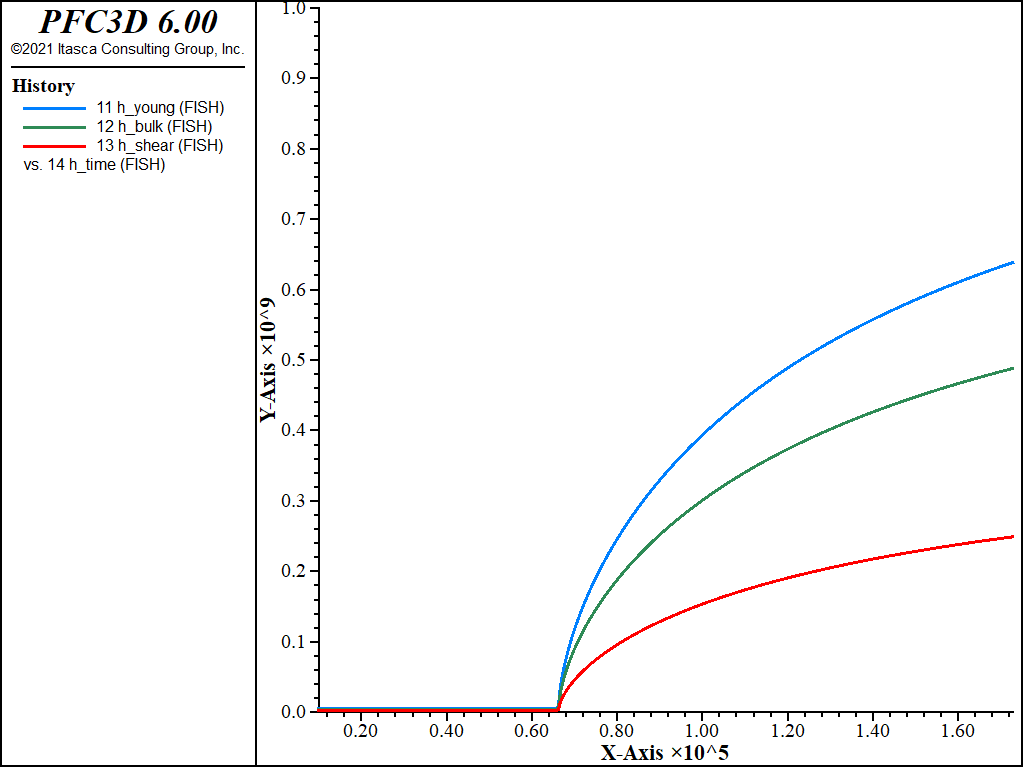
Figure 5: Evolution of the elastic parameters for the center zone of the concrete inclusion as a function of the concrete age.
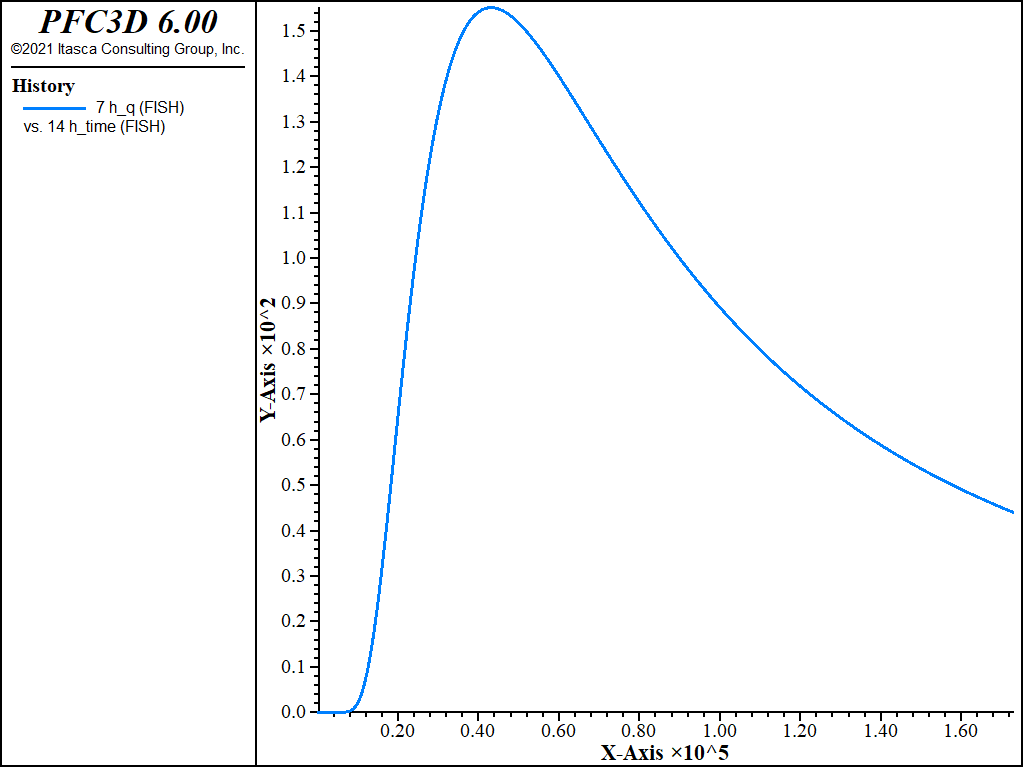
Figure 6: Evolution of the hydration heat for the center zone of the concrete inclusion as a function of the concrete age.
Data File
;--------------------------------------------------------------
; Concrete inclusion in an elastic, thermal isotropic medium
;--------------------------------------------------------------
model new
model largestrain off
model title "Concrete inclusion in an elastic, thermal isotropic medium"
fish automatic-create off
model configure thermal
;
zone create brick size 11 1 11
zone face skin
zone group 'concrete' range position (4,0,4) (7,1,7)
zone cmodel assign hydration-drucker-prager range group 'concrete'
zone thermal cmodel assign hydration range group 'concrete'
zone cmodel assign elastic range group 'concrete' not
zone thermal cmodel assign isotropic range group 'concrete' not
;
zone property densit=2000 bulk=1e9 shear=0.7e9
zone thermal property conductivity=20.0 expansion=1e-4 specific-heat=0.2
; Mechanical hydration
zone property bulk-reference=0.98e9 shear-reference=0.50e9 range group 'concrete'
zone property constant-c=0.4 constant-a=0.6 range group 'concrete'
zone property hydration-minimum=0.20 tension-reference=2.0e6 range group 'concrete'
zone property hydration-difference-minimum=1e-4 range group 'concrete'
; Thermal hydration
zone thermal property conductivity=2.0 expansion=1e-5 specific-heat=0.2 range group 'concrete'
zone thermal property density-cement=330 constant-jonasson-b=-1.114 constant-jonasson-t1=7.2e4 range group 'concrete'
zone thermal property constant-gas=8.314 temperature-reference=293 hydration-grade-maximum=1.0 hydration-temperature-maximum=1e4 range group 'concrete'
zone thermal property constant-energy-1=33.5 constant-energy-dt=1.47 constant-energy-halftime=273 constant-heat-1=0.2 range group 'concrete'
zone thermal property hydration-binding-maximum=1e5 constant-conductivity-1=2.0 range group 'concrete'
;
zone gridpoint initialize temperature 300
zone face apply temperature 300 range group 'Top' or 'Bottom' or 'West' or 'East'
;
zone face apply velocity-x 0 range group 'West' or 'East'
zone face apply velocity-y 0 range group 'North' or 'South'
zone face apply velocity-z 0 range group 'Top' or 'Bottom'
;
zone history temperature position (1,0,5)
zone history temperature position (2,0,5)
zone history temperature position (3,0,5)
zone history temperature position (4,0,5)
zone history temperature position (5,0,5)
[global hzp = zone.near.all(6.5,0.5,6.5)]
fish define h_alpha
global h_alpha = zone.therm.prop(hzp,'hydration-grade')
global h_q = zone.therm.prop(hzp,'hydration-rate')
global h_te = zone.therm.prop(hzp,'age-concrete-effective')
global h_tension = zone.prop(hzp,'tension')
global h_comp = zone.prop(hzp,'compression')
global h_young = zone.prop(hzp,'young')
global h_bulk = zone.prop(hzp,'bulk')
global h_shear = zone.prop(hzp,'shear')
global h_time = thermal.time.total
end
fish history @h_alpha
fish history @h_q
fish history @h_te
fish history @h_tension
fish history @h_comp
fish history @h_young
fish history @h_bulk
fish history @h_shear
fish history @h_time
;
zone geometry-update 1
history interval 100
model solve time-total [2*24*3600]
model save 'concreteInclusion'
return
| Was this helpful? ... | PFC 6.0 © 2019, Itasca | Updated: Nov 19, 2021 |