Power-Mohr Model: Cylindrical Cavity
Note
To view this project in 3DEC, use the menu command . The project’s main data files are shown at the end of this example.
The problem of radial creep of an infinitely long, thick-walled cylinder, presented in Power Model: Cylindrical Cavity, is analyzed again in this example, this time considering a viscoplastic material. The material viscous behavior is characterized by a single-component power law, and the plastic behavior by a Mohr-Coulomb yield criterion. The plastic properties of the material are associated, the cohesion is 15 MPa, and the friction angle is 15 degrees. The steady-state solution is compared to the analytical solution for a viscoelastic material obeying the same viscous law (see Power Model: Cylindrical Cavity).
The model geometry, material properties, and initial and boundary conditions are the same as those used in Power Model: Cylindrical Cavity. The numerical simulation is performed in three stages. In the first stage, the cohesion is set to a high value and the model is run to elastic equilibrium. In the second stage, the actual values for cohesion, friction, and dilation are assigned to the zones, and the new equilibrium state is calculated. The velocities are reset to zero before performing the creep calculation (stage 3).
The viscoelastic analytical solution is given by the FISH function powcyl, included in the project. The results for radial and hoop stresses and plastic state at the end of the simulation are presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2. As may be observed on the plots, the region around the internal cavity is yielding, and the effect of plasticity translates in a reduction of the hoop stress magnitude in the plastic domain.
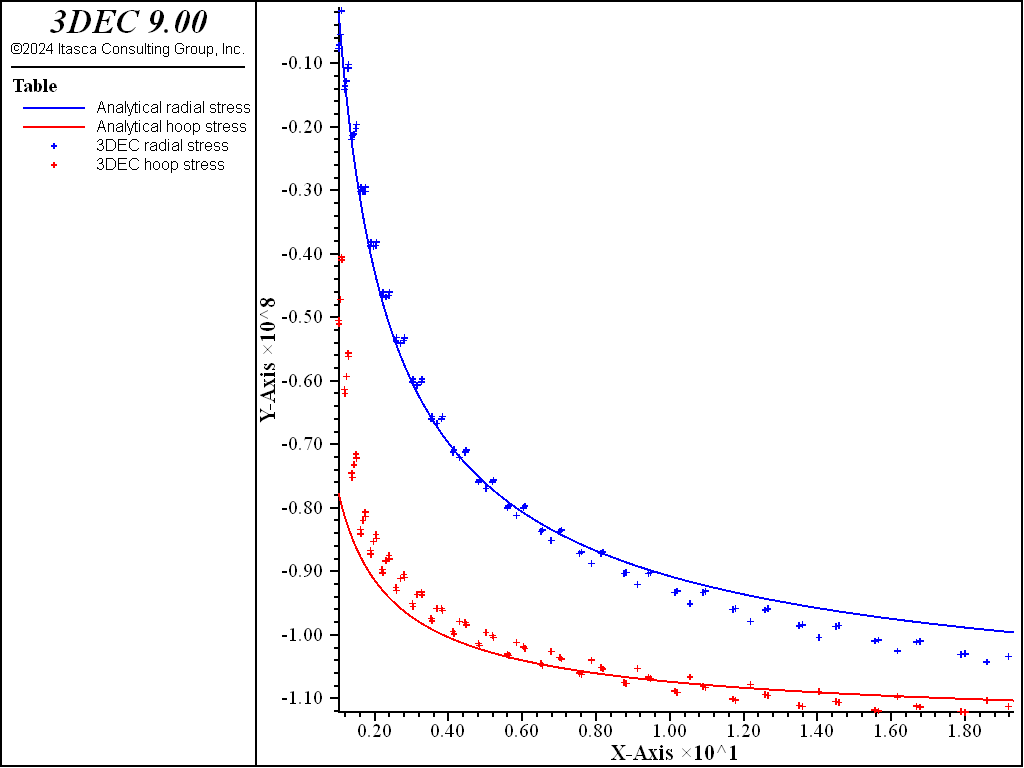
Figure 1: Radial and hoop stress at steady state—comparison between viscoplastic solutions (lines) and viscoelastic solutions (symbols).
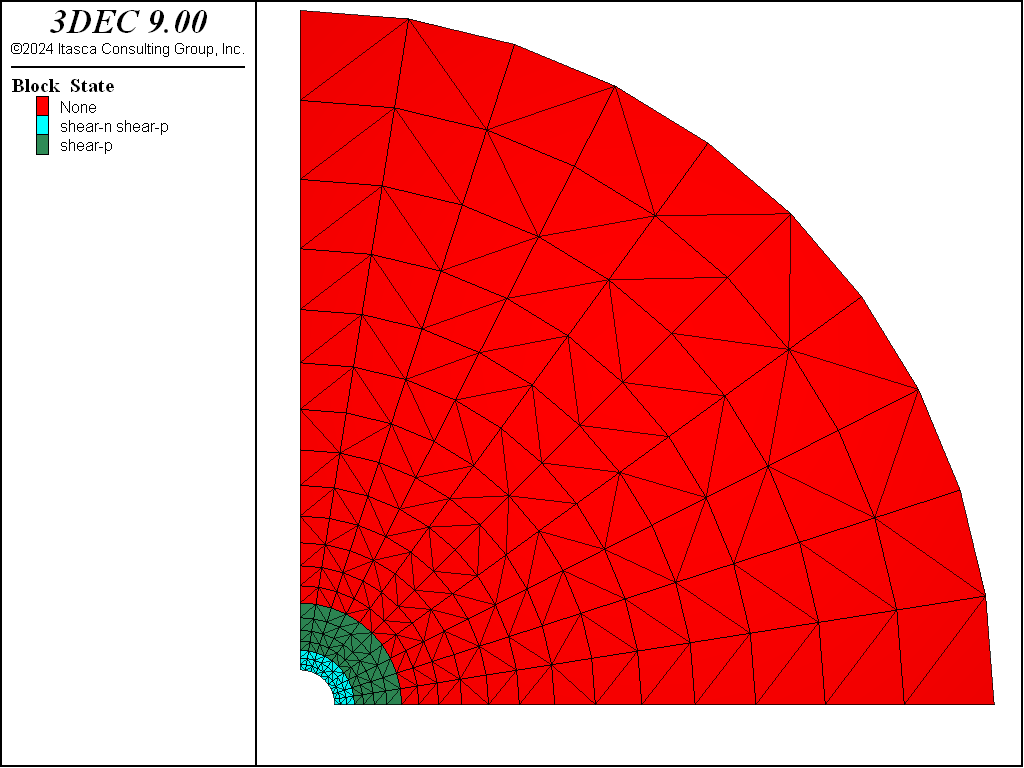
Figure 2: Plastic state at steady state.
Data Files
CylindricalCavityPowerMohr.dat
;------------------------------------------------------------
; cylindrical cavity -- power-mohr model
;-------------------------------------------------------------------
model new
fish automatic-create off
model title "Power-Mohr Creep Model --- Cylindrical Cavity"
model configure creep
model large-strain off
block tolerance 0.001
;
program call 'cylinder.fis'
[r_inner = 1.0]
[r_outer = 20.0]
[nr = 20]
[nd = 1]
[nc = 10]
[ratio = 1.1]
[length = 0.1]
[cylinder]
block join on
;block zone generate center 0 0 0 edgelength-center 0.1 edgelength-dist 2.5 distance 20
block zone generate hexahedra
block zone cmodel power-mohr
; Properties and stresses in Pascal units (not MPa)
block zone property density 2500 bulk=1e9 shear=3e8
block zone property constant-1=1e-25 exponent-1=3
block zone property cohesion 1e15 tension 1e15
;
; apply stress first!
block face apply stress -100e6 -100e6 -100e6 0 0 0 ...
range cylinder end-1 0 0 0 end-2 0 0 -1 radius 19 21
block gridpoint apply velocity-x 0 range position-x 0
block gridpoint apply velocity-y 0 range position-y 0
block gridpoint apply velocity-z 0 range position-z -1 0
block zone initialize stress xx -100e6 yy -100e6 zz -100e6
;
model creep active off
model solve ratio 1e-7
block zone property cohesion 1.5e7 friction 15 dilation 15 tension 1e15
model solve ratio 1e-7
model save 'cyl_1'
model history mechanical unbalanced-maximum
block history velocity-x position 1 0 0
block history velocity-x position 20 0 0
block history displacement-x position 1 0 0
block history displacement-x position 20 0 0
block history stress-xx position 1 0 0
block history stress-yy position 1 0 0
block history stress-zz position 1 0 0
model history creep time-total
model history timestep
;
block gridpoint initialize velocity (0,0,0)
model creep active on
model creep timestep starting 1.0e-6
model creep timestep minimum 1.0e-6
model creep timestep maximum 0.1
model solve time-total 200
model save 'cyl_2'
; compare analytic solution......
program call 'solution.fis' suppress
table '1' label '3DEC x-velocity'
table '11' label 'Analytical x-velocity'
table '2' label '3DEC radial stress'
table '12' label 'Analytical radial stress'
table '3' label '3DEC hoop stress'
table '13' label 'Analytical hoop stress'
table '4' label '3DEC out-of-plane stress'
table '14' label 'Analytical out-of-plane stress'
model save 'cylindrical-cavity-power-mohr'
program return
| Was this helpful? ... | Itasca Software © 2024, Itasca | Updated: Nov 12, 2025 |
