Rough Square Footing on a Cohesive Frictionless Material
Problem Statement
Note
The project file for this example may be viewed/run in 3DEC.[1] The main data files used are shown at the end of this example.
This problem is concerned with the numerical determination of the bearing capacity of a rough rectangular footing on a cohesive frictionless material (Tresca model).
A footing of width \(2a\) and length \(2b\) is located on an elasto-plastic Tresca material with the following properties:
shear modulus (\(G\)): 1 GPa
bulk modulus (\(K\)): 2 GPa
cohesion (\(c\)): 0.1 MPa
friction angle (\(\phi\)): 0°
dilation angle (\(\psi\)): 0°
Upper- and Lower-Bound Solutions
The problem is truly three-dimensional and, although no exact solution is available, upper and lower bounds for the bearing capacity, \(q\), defined as the average footing pressure at failure, have been derived using limit analysis (see, for example, Chen 1975). The upper bound, \(q^u\), obtained using the failure mechanism of Shield and Drucker (1953), has the form
in which \(c\) is the cohesion of the material. The lower bound, \(q^l\), which corresponds to the bearing capacity of a strip footing, has the value
3DEC Model
In the numerical example, the footing is square and represented by an area with dimensions \(a\) = 3 m and \(b\) = 3 m. We take advantage of quarter symmetry, and a parallelepiped domain of 15 m × 15 m × 10 m (as sketched in Figure 1) is used in the numerical simulation. The system of coordinate axes is selected with the \(x\)- and \(y\)-axes in the horizontal plane of the footing, and the \(z\)-axis pointing up in the vertical direction (see Figure 1).
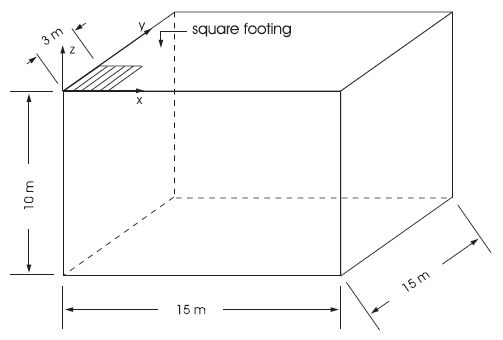
Figure 1: Domain for 3DEC simulation — quarter symmetry.
The boundary conditions applied to this domain are sketched in Figure 2.
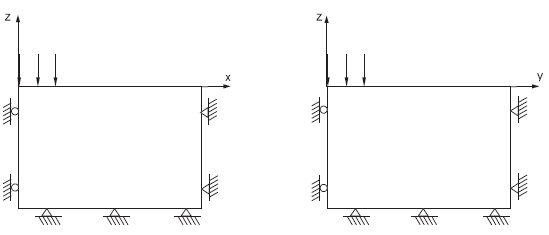
Figure 2: Boundary conditions for 3DEC analysis — quarter symmetry.
The displacements of the far \(x\)-, \(y\)-, and \(z\)-boundaries are restricted in all directions, and the displacements of the symmetry boundaries corresponding to the planes at \(x\) = 0 and \(y\) = 0 are restricted in the \(x\)- and \(y\)-direction, respectively. The slab is rough: displacements are restricted in the \(x\)- and \(y\)-directions; and a velocity is applied in the negative \(z\)-direction on a 3 m × 3 m area to simulate loading of the footing.
The model contains one block discretized into 22,500 quad zones. (The model geometry and its discretization are shown in Figure 3.) The area representing the footing covers a total of 3 × 3 zones. A velocity of magnitude 10−2 m/s is applied at the nodes in contact with the footing representation, for a total of 8000 steps.
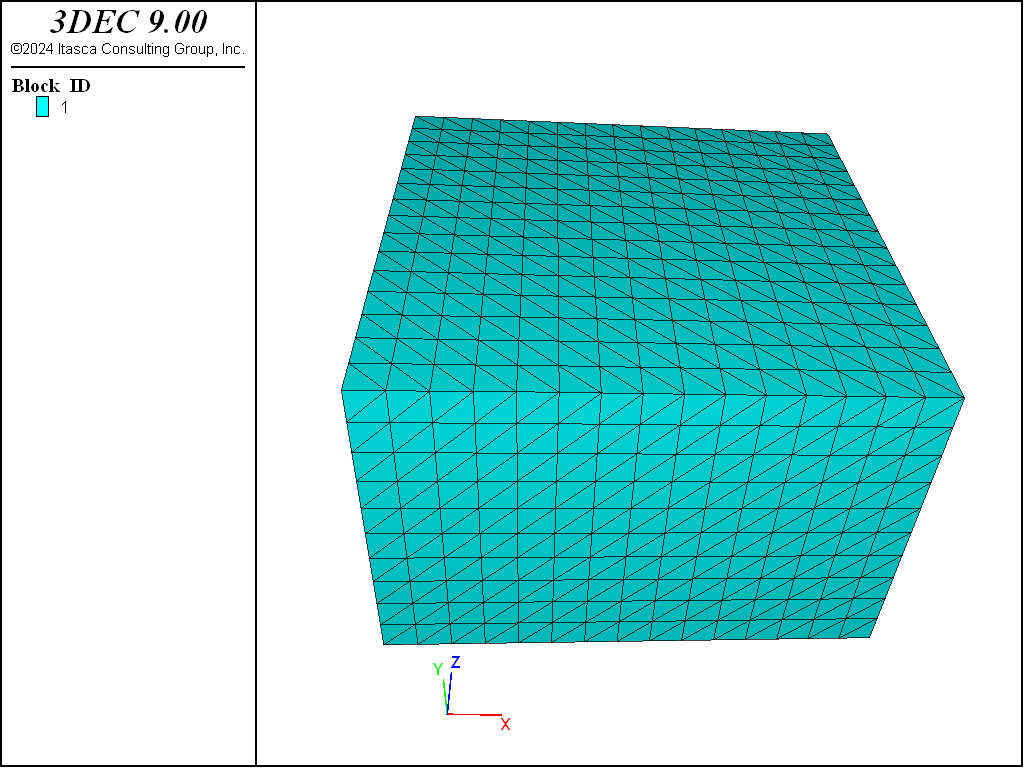
Figure 3: 3DEC grid — quarter symmetry.
Results and Discussion
The load-displacement curve corresponding to the numerical simulation is presented in Figure 4. History 2 is the normalized average footing pressure, \(p/c\); history 3 is the normalized upper-bound value for the bearing capacity, \(q^u /c\), plotted versus the normalized vertical displacement, \(u_z /a\), at the center of the footing. The numerical value of the bearing capacity is 578 kPa. This value is very close to the theoretical upper-bound value of 571 kPa (relative absolute difference of 1.2%). The displacement field at the end of the numerical simulation is illustrated in Figure 5.
The data file used to generate the numerical solution is “foot-hex.dat”. The FISH function load in “foot.fis” computes the normalized average footing pressure, \(p/c\).
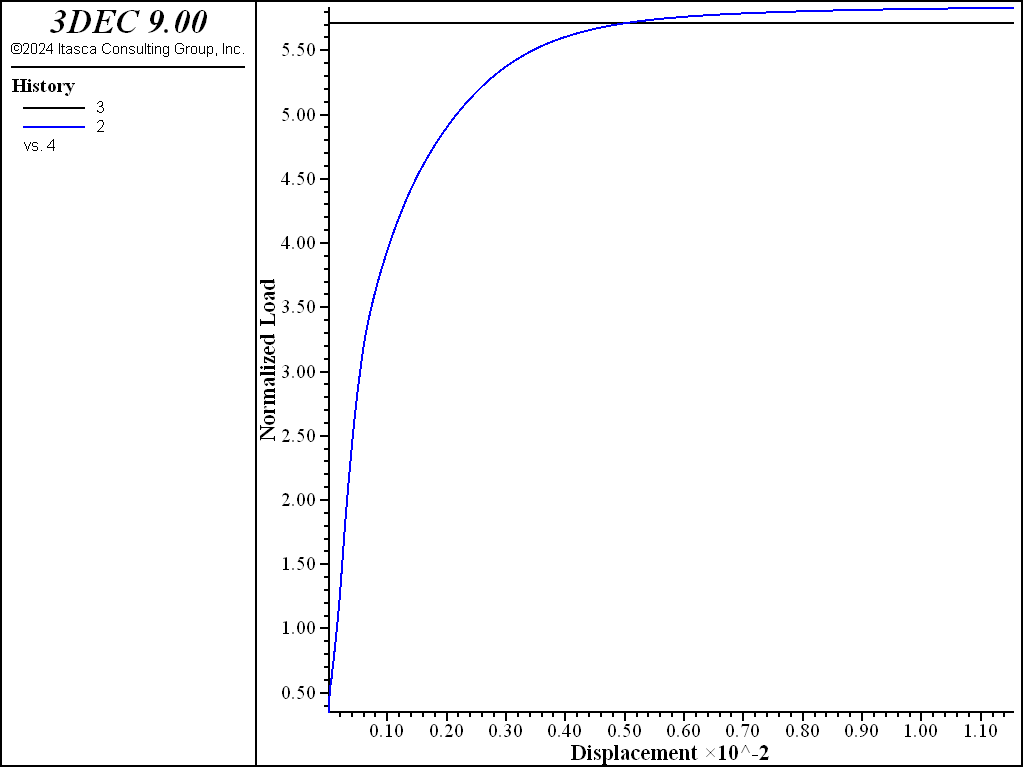
Figure 4: Load-displacement curve.
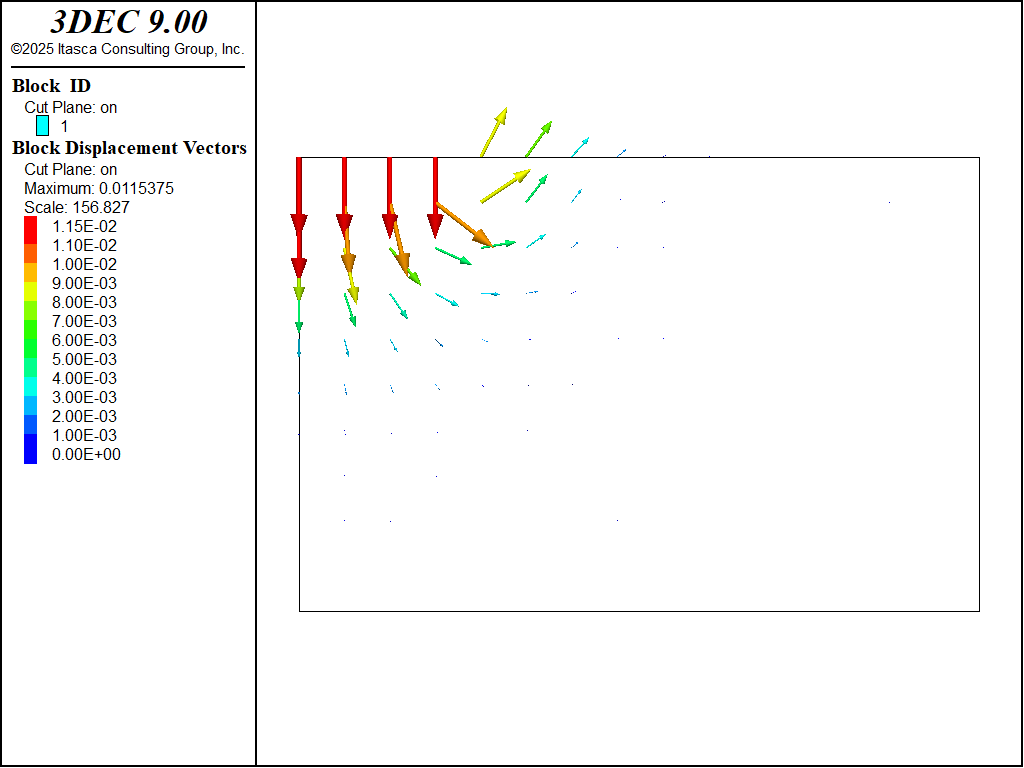
Figure 5: 3DEC plot of displacement vectors in the cross-section.
The indentation was solved using high-order tetrahedral elements. Figure 6 shows the load displacement curve. The value of the bearing capacity is 619 kPa. This is slightly greater than the theoretical upper bound (relative absolute difference of 8%). The result of the higher-order elements is not as accurate as the mixed discretization in this case.
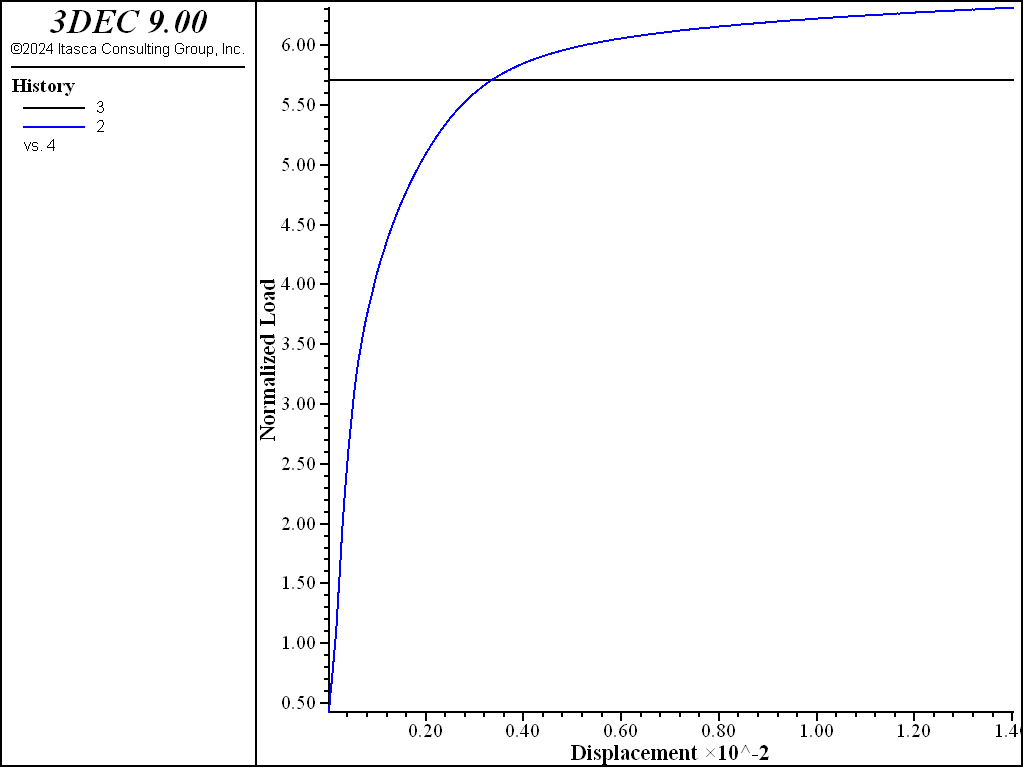
Figure 6: Load displacement curve for high-order elements.
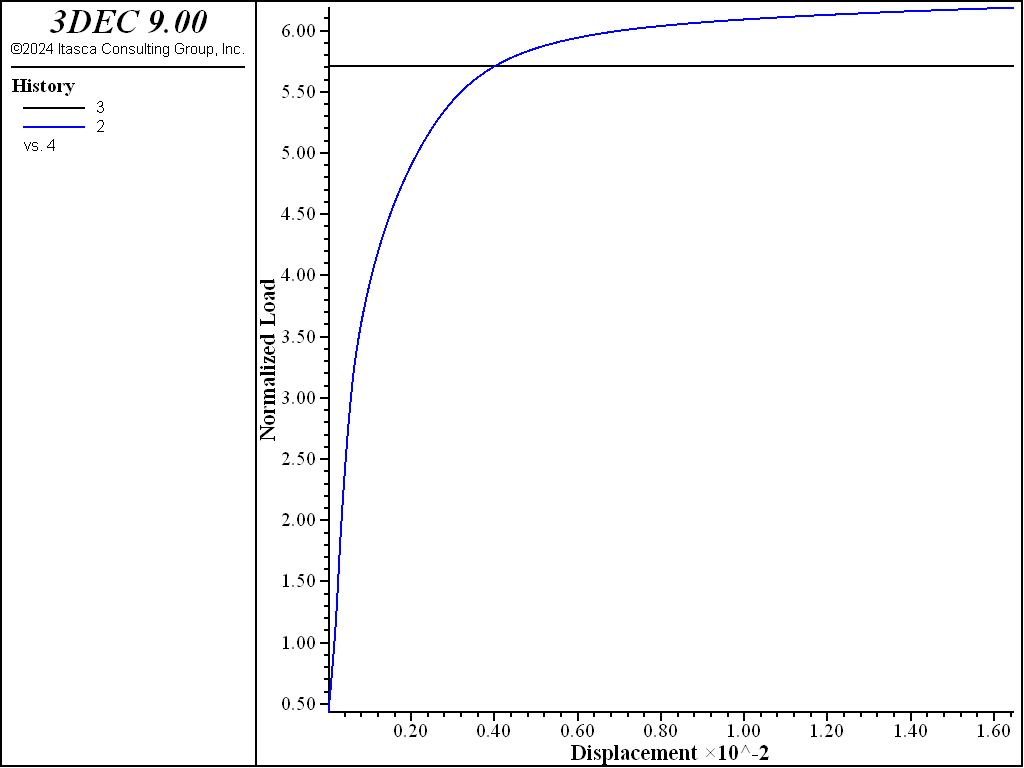
Figure 7: Load displacement curve for nodal mixed discretization.
Figure 7 shows the result when using nodal mixed discretization (NMD). This gives results very similar to those obtained from a model using higher-order elements.
The same problem was also solved using regular tetrahedral zoning. However, the indentation pressure calculated with this model (shown in Figure 8) does not converge to a finite value (i.e., the pressure continuously increases as a function of vertical displacement). This problem illustrates the major advantage of quad zoning and mixed discretization over regular tetrahedral zones: the model with tetrahedral zones does not produce an accurate solution for the calculation of a limit load in elasto-plastic models.
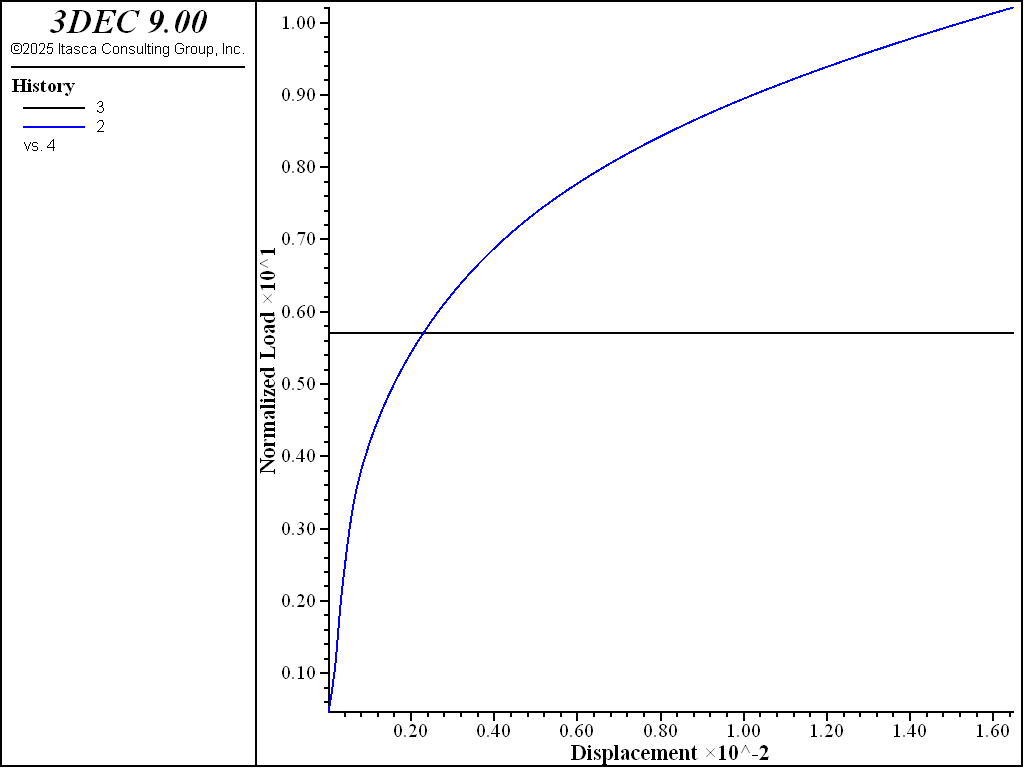
Figure 8: Load-displacement curve calculated using tetrahedral zoning.
References
Chen, W.-F. “Bearing Capacity of Square, Rectangular and Circular Footings,” in Limit Analysis and Soil Plasticity, Developments in Geotechnical Engineering 7, Ch. 7, pp. 295-340. New York: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co. (1975).
Shield, R. T., and D. C. Drucker. “The Application of Limit Analysis to Punch-Indentation Problems,” J. Appl. Mech., 20, 453-460 (1953).
Data Files
foot-hex.dat
;==========================================================================
; verification test -- 3dec modeling indentation of rectangular area in an
; infinite, isotropic, homogeneous, Tresca medium
;
; Mixed discretization using quadrilateral zoning
; Mohr-Coulomb blocks
;
;==========================================================================
model new
model large-strain on
block create brick 0 15 0 15 0 10
;
; --- zoning of blocks ---
;
block zone generate hexahedra divisions 10 15 15
;
; --- material properties ---
;
block zone cmodel assign mohr-coulomb
block zone property bulk 2.e9 shear 1.e9 density 2600 ...
cohesion 1.e5 tension 1e20
block contact material-table default property stiffness-normal 1e10 ...
stiffness-shear 1e10
;
; --- boundary conditions ---
block gridpoint apply velocity-x 0 range position-x 0
block gridpoint apply velocity-y 0 range position-y 0
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-x 15
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-y 15
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-z 0
block gridpoint group 'foot' range position-x -0.1 3.1 ...
position-y -0.1 3.1 position-z 10
block gridpoint apply velocity-x 0. velocity-y 0. velocity-z -1e-2 ...
range group 'foot'
program call 'foot.fis'
[setup('foot')]
model history mechanical unbalanced-maximum
fish history load
fish history solution
fish history disp
history name '2' label '3DEC'
history name '3' label 'Analytic'
history name '4' label 'Displacement'
model cycle 8000
model save 'foot-hex'
program return
foot.fis
fish automatic-create off
;---------------------------------------------------------------------
; Defines FISH functions that monitor total footing load & displacement
;---------------------------------------------------------------------
fish define setup(name)
global points = map
global solution = (5.24+0.47)
global cohesion = 1e5
; Find all gridpoints on footing and store them in the map
global n = 0
loop foreach local gp block.gp.list
if block.gp.isgroup(gp,name) then
points(map.size(points)) = gp ; Store in map, random unique index
local height = block.gp.pos.z(gp) ; Store height of footing
end_if
end_loop
; Find first gridpoint to the right of the footing, at the same height
local xnext = 20.0
loop foreach gp block.gp.list
if block.gp.isgroup(gp,name)==false then
if block.gp.pos.z(gp)==height then
if block.gp.pos.y(gp)==0
xnext = math.min(xnext,block.gp.pos.x(gp))
endif
end_if
end_if
end_loop
global width = (3.0 + xnext) * 0.5 ; Adjusted width
global center = block.gp.near(0,0,10)
end
;---------------------------------------------------------------------
; p_load : average footing pressure / c
; c_disp : magnitude of vertical displacement at footing center / a
;---------------------------------------------------------------------
fish define load
local accum = 0.0
loop foreach local gp points
accum = accum - block.gp.force.reaction.z(gp)
end_loop
global disp = -block.gp.disp.z(center)
load = accum / (width * width * cohesion)
end
foot-h0.dat
;==========================================================================
; verification test -- 3dec modeling indentation of rectangular area in an
; infinite, isotropic, homogeneous, Tresca medium
;
; higher order tetrahedral zoning (edgelength 1)
; Mohr-Coulomb blocks
;
;==========================================================================
model new
model configure highorder
model large-strain on
block create brick 0 15 0 15 0 10
;
; --- zoning of blocks ---
;
block cut joint-set dip 90 dip-direction 90 origin 3 0 0
block cut joint-set dip 90 dip-direction 180 origin 0 3 0
block join
block zone generate edgelength 1.0
block zone generate high-order-tetra
;
; --- material properties ---
;
block zone cmodel assign mohr-coulomb
block zone property bulk 2.e9 shear 1.e9 density 2600 ...
cohesion 1.e5 tension 1e20
block contact material-table default property stiffness-normal 1e10 ...
stiffness-shear 1e10
;
; --- boundary conditions ---
block gridpoint apply velocity-x 0 range position-x 0
block gridpoint apply velocity-y 0 range position-y 0
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-x 15
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-y 15
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-z 0
block gridpoint group 'foot' ...
range position-x -0.1 3.1 position-y -0.1 3.1 position-z 10
block gridpoint apply velocity-x 0. velocity-y 0. velocity-z -1e-2 ...
range group 'foot'
program call 'foot.fis'
[setup('foot')]
model history mechanical unbalanced-maximum
fish history load
fish history solution
fish history disp
history name '2' label '3DEC'
history name '3' label 'Analytic'
history name '4' label 'Displacement'
model cycle 8000
model save 'foot-ho'
program return
foot-nmd.dat
;==========================================================================
; verification test -- 3dec modeling indentation of rectangular area in an
; infinite, isotropic, homogeneous, Tresca medium
;
; Nodal Mixed Discretization
; dll Mohr-Coulomb blocks
;
;==========================================================================
model new
model large-strain on
block create brick 0 15 0 15 0 10
; --- zoning of blocks ---
;
block cut joint-set dip 90 dip-direction 90 origin 3 0 0
block cut joint-set dip 90 dip-direction 180 origin 0 3 0
block join
block zone generate edgelength 1.0
;
; --- material properties ---
;
block zone cmodel assign mohr-coulomb
block zone property bulk 2.e9 shear 1.e9 density 2600 ...
cohesion 1.e5 tension 1e20
block contact material-table default property stiffness-normal 1e10 ...
stiffness-shear 1e10
;
; --- boundary conditions ---
block gridpoint apply velocity-x 0 range position-x 0
block gridpoint apply velocity-y 0 range position-y 0
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-x 15
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-y 15
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-z 0
block gridpoint group 'foot' range position-x -0.1 3.1 ...
position-y -0.1 3.1 position-z 10
block gridpoint apply velocity-x 0. velocity-y 0. velocity-z -1e-2 ...
range group 'foot'
program call 'foot.fis'
[setup('foot')]
model history mechanical unbalanced-maximum
fish history load
fish history solution
fish history disp
history name '2' label '3DEC'
history name '3' label 'Analytic'
history name '4' label 'Displacement'
block zone nodal-mixed-discretization on
model cycle 8000
model save 'foot-nmd'
program return
foot-tet.dat
;==========================================================================
; verification test -- 3dec modeling indentation of rectangular area in an
; infinite, isotropic, homogeneous, Tresca medium
;
; simple tetrahedral zoning (edgelength 1)
; Mohr-Coulomb blocks
;
;==========================================================================
model new
model large-strain on
block create brick 0 15 0 15 0 10
;
; --- zoning of blocks ---
;
block cut joint-set dip 90 dip-direction 90 origin 3 0 0
block cut joint-set dip 90 dip-direction 180 origin 0 3 0
block join
block zone generate edgelength 1.0
;
; --- material properties ---
;
block zone cmodel assign mohr-coulomb
block zone property bulk 2.e9 shear 1.e9 density 2600 ...
cohesion 1.e5 tension 1e20
block contact material-table default property stiffness-normal 1e10 ...
stiffness-shear 1e10
;
; --- boundary conditions ---
block gridpoint apply velocity-x 0 range position-x 0
block gridpoint apply velocity-y 0 range position-y 0
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-x 15
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-y 15
block gridpoint apply velocity 0 0 0 range position-z 0
block gridpoint group 'foot' range position-x -0.1 3.1 ...
position-y -0.1 3.1 position-z 10
block gridpoint apply velocity-x 0. velocity-y 0. velocity-z -1e-2 ...
range group 'foot'
program call 'foot.fis'
[setup('foot')]
model history mechanical unbalanced-maximum
fish history load
fish history solution
fish history disp
history name '2' label '3DEC'
history name '3' label 'Analytic'
history name '4' label 'Displacement'
model cycle 8000
model save 'foot-tet'
program return
Endnote
| Was this helpful? ... | Itasca Software © 2024, Itasca | Updated: Nov 12, 2025 |
