FLAC3D Theory and Background • Fluid-Mechanical Interaction
Semi-confined Aquifer
Note
The project file for this example is available to be viewed/run in FLAC3D. The project’s main data files are shown at the end of this example.
Fluid leakage into a shallow semi-confined aquifer can be modeled with FLAC3D using the
zone face apply leakage command. This is demonstrated for the example defined by the sketch in
Figure 1. The aquifer has a length \(L\), height \(H\), and
rests on an impermeable base. Fluid flow obeys Darcy’s law; the mobility coefficient \(k\) is
homogeneous and isotropic. The semi-permeable top layer has permeability \(k_*\), and thickness
\(H_*\). The effect of gravity is neglected in this example. Fluid pressure at the top of the leaky
layer is constant and equal to \(p_*\). The lateral fluid-flow conditions correspond to a constant
pressure \(p_0\) at the left boundary, and \(p_1\) at the right.
The objective is to determine the steady-state pore-pressure profile and total leakage into the aquifer. The general solution of pore pressure for a shallow semi-confined aquifer has the form (see Strack 1989)
where \(\lambda\) is the seepage factor, which has the dimension of length and is defined as \(\lambda = \sqrt{k H H_*/k_*}\); \(A\) and \(B\) are constants determined from the pressure boundary conditions.
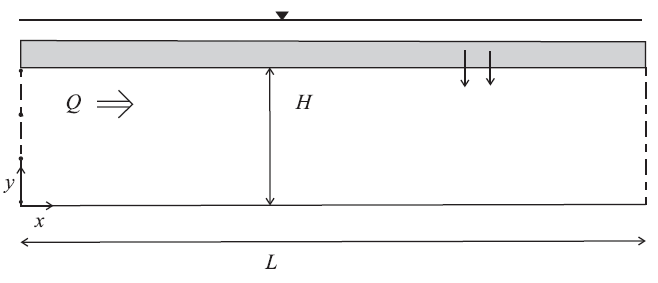
Figure 1: Shallow semi-confined aquifer.
The boundary conditions for this problem are
\(p = p_0\) |
at |
\(x = 0\) |
\(p = p_1\) |
at |
\(x = L\) |
The pore pressure solution is
where
The steady state discharge over the height of the aquifer is obtained from Darcy’s law:
After differentiation of Equation (2) with respect to \(x\), and substitution into Equation (5), we obtain
The total amount of leakage into the aquifer is, by continuity of flow, equal to the difference between the discharge leaving at \(x\) = \(L\) and that entering at \(x\) = 0. Using Equation (6), we obtain, after some manipulation,
Equation (6) and Equation (7) are used for comparison to the FLAC3D solution.
The FLAC3D data file for this problem is listed in
“SemiConfinedAquifer.dat”. The analytical solution is programmed
in FISH as part of the data file. The FLAC3D model is a 20 zone by 2 zone mesh with a constant pore
pressure of \(p_0\) = 20 kPa applied at the left boundary, \(x\) = 0, and a constant pore
pressure of \(p_1\) = 10 kPa applied at the right boundary, \(x\) = 20 m. A leaky aquifer
boundary condition is applied along the top boundary of the model, \(y\) = 1 m, using the
zone face apply leakage command. The pore pressure at the top is \(p_*\) = 1.8 kPa, and the
leakage coefficient \(h\) (see this equation), is evaluated to be \(k_*/H_*\) = 2.98 ×
10-9 m3 /(N sec), based on the properties of the leaky layer.
The fluid-flow calculation mode is turned on, the
mechanical calculation mode is turned off, and the simulation is run until steady-state flow is reached.
The FISH function checkit compares the amount of leakage calculated by FLAC3D to the solution of (7) at steady-state flow. The difference is printed (in a FISH dialog message) to be 0.03%. The analytical and numerical pore pressure profiles recorded along the base of the model, from \(x\) = 0 to \(x\) = 20, are compared in Figure 2.
The same model is run twice more - once with the implicit servo active and once using the zone fluid steady-state command to immediately find the steady state. The pore-pressure distribution of all three methods are the same to within 0.1%.
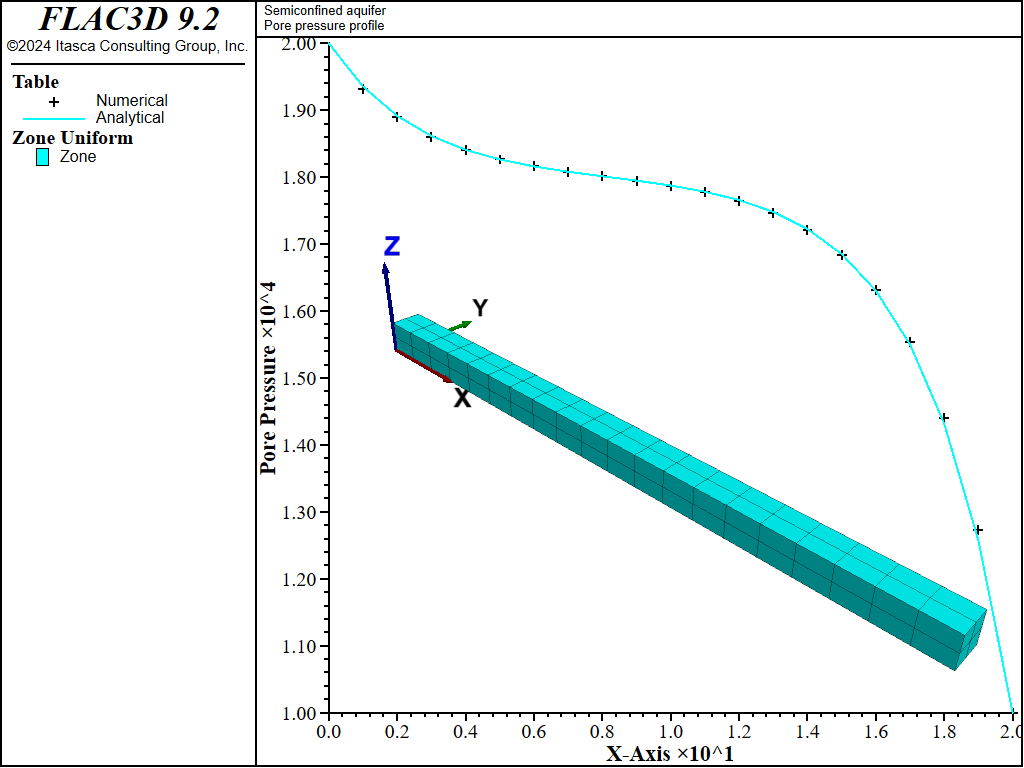
Figure 2: Pore pressure profile.
Reference
Strack, O. D. L. Groundwater Mechanics. New Jersey: Prentice Hall (1989).
pagebreak
Data File
SemiConfinedAquifer.dat
; file for 'Semiconfined aquifer'
model new
model title 'Semiconfined aquifer'
; Geometry
zone create brick point 0 (0,0,0) point 1 (20,0,0) point 2 (0,1,0) ...
point 3 (0,0,1) size 20 2 2
zone face skin
; Constitutive model and properties
model configure fluid-flow
zone fluid property porosity=0.04 mobility-coefficient=2e-8 ...
fluid-modulus=2e9
; --- boundary conditions ---
zone face apply leakage 1.8e4 3e-9 range group 'Top'
zone face apply pore-pressure 2e4 range group 'West'
zone face apply pore-pressure 1e4 range group 'East'
model save 'start'
; --- explicit fluid flow solution ---
model solve-fluid time 1
model save 'confaquifer'
; --- Implicit fluid flow solution ---
model restore 'start'
zone fluid implicit servo on
model solve-fluid time 1
model save 'confaquifer-imp'
; --- Steady state flow solution ---
model restore 'start'
zone fluid steady-state
model save 'confaquifer-steady'
⇐ Pressuremeter Test | Verification of Concepts, and Modeling Techniques for Specific Applications ⇒
| Was this helpful? ... | Itasca Software © 2024, Itasca | Updated: Dec 05, 2024 |
