FLAC3D Theory and Background • Fluid-Mechanical Interaction
Transient Fluid Flow to a Well in a Shallow Confined Aquifer
Note
The project file for this example is available to be viewed/run in FLAC3D. The project’s main data files are shown at the end of this example.
A shallow confined aquifer of large horizontal extent is characterized by a uniform initial pore pressure, \(p_0\), and initial isotropic stress, \({\sigma}_{zz}^0\). A well, fully penetrating the aquifer, is producing water at a constant rate, \(q\), per unit depth from time, \(t = t_0\). The elastic porous medium is homogeneous and isotropic, and the flow of groundwater is governed by Darcy’s law. Transient effects are linked to the compressibility of water and the soil matrix. In this problem, the effect of pore-pressure changes are small compared to the overburden, and the vertical stress in the aquifer may be assumed to remain constant with time. Also, horizontal strains are neglected compared to the vertical ones. The conditions of fluid flow to the well are illustrated schematically in Figure 1. The numerical solution to this problem is presented using both coupled and uncoupled modeling approaches.
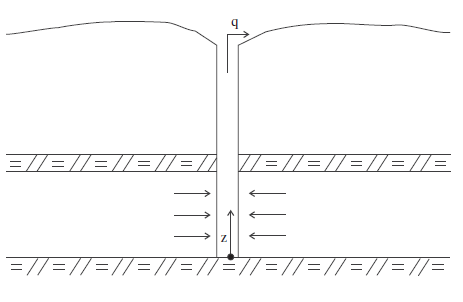
Figure 1: Flow to a well in a shallow confined aquifer.
A cylindrical system of coordinates is chosen with the \(z\)-axis pointing upward in the direction of the well axis. Substitution of the transport law in the fluid mass-balance equation gives, taking into consideration that \({\epsilon}_{rr} = {\epsilon}_{\theta \theta}\) = 0,
where \(k\) is the homogeneous permeability coefficient, \(M\) is the Biot modulus, and \(\alpha\) is the Biot coefficient.
Partial differentiation, with respect to time, of the elastic constitutive relation \({\sigma}_{zz} - {\sigma}_{zz}^0 + \alpha(p - p_0) = \alpha_1 {\epsilon}_{zz}\) yields, for constant \({\sigma}_{zz}\),
where \(\alpha_1 = K + 4/3 G\).
Using this last equation to express \({\epsilon}_{zz}\) in terms of \(p\) in Equation (1), we obtain, after some manipulations,
where \(c = k/S\) is the diffusion coefficient, \(S = 1/M + {\alpha}^2 / {\alpha_1}\) is the storage coefficient, and, with the problem being axisymmetric and not dependent on \(z\), the Laplacian of \(p\) may be expressed as
The solution to this differential equation with boundary conditions
is due to Theis (1935). It has the form
where \(\hat{p} = p k/q\). The dimensionless variable \(u\) is given by
and \(E_1\) is the exponential integral, defined as
The vertical displacement may be obtained by integration of the equilibrium equation \(\partial {\sigma}_{zz}/\partial z\) = 0 after expressing \(\sigma_{zz}\) in terms of \(\epsilon_{zz}\) by means of the mechanical constitutive equation and substituting \(\partial \epsilon_{zz} / \partial z\) for \(\epsilon_{zz}\). This yields, after substitution of the boundary condition, and using Equation (7),
where \({\hat{u}}_z = u k \alpha_1 /(\alpha q H)\) and \({\hat{x}} = z/H\).
The stresses are derived from the mechanical constitutive equations and Equation (7) for \(\hat{p}\). They have the form
where \(\hat{\sigma} = \sigma k \alpha_1 / (q \alpha G)\).
The FLAC3D grid for this problem corresponds to a nine-degree wedge in a hollow cylinder of unit height. The axis and radius of the well correspond to cylinder axis and radius, respectively. The cylinder outer radius is selected as 100 m to model the far boundary of the flow domain. Figure 2 shows the FLAC3D grid.
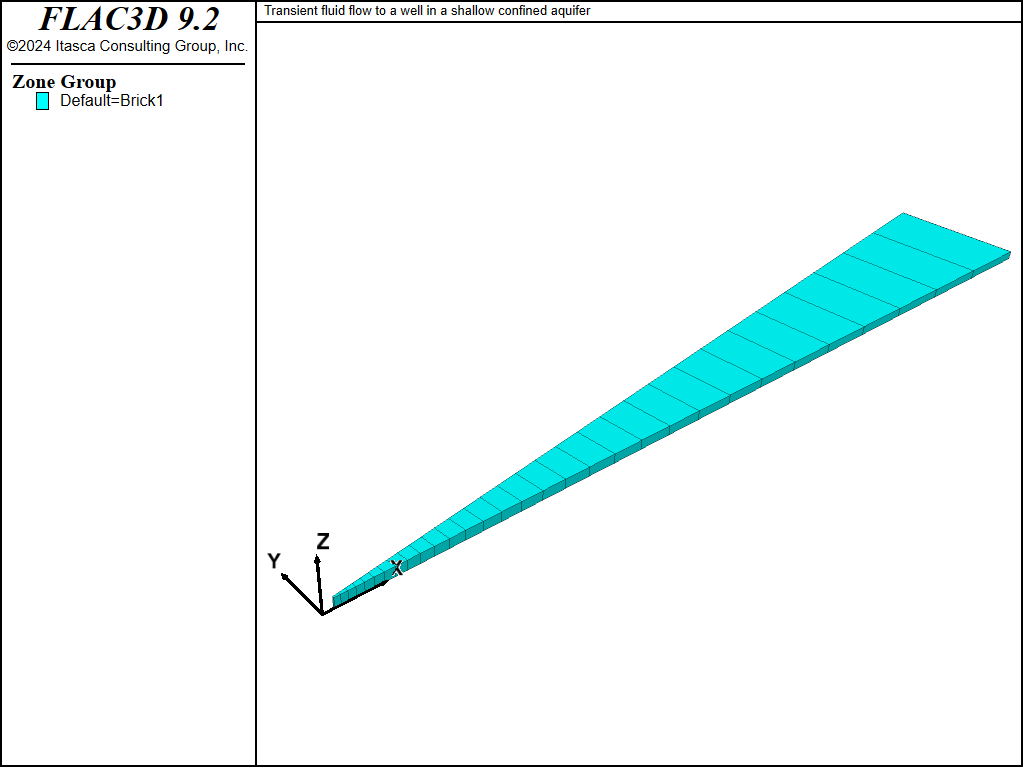
Figure 2: FLAC3D grid for a well in a shallow aquifer.
A total of 31 zones are used, lined up, and graded in the radial direction. The displacements are fixed in the radial and tangential directions, and in the vertical direction at the cylinder base. A vertical pressure of magnitude \(- \sigma_{zz}^0\) is applied at the top of the model.
The properties for this example are defined:
dry bulk modulus (\(K\)) |
118 MPa |
dry shear modulus (\(G\)) |
71 MPa |
water bulk modulus (\(K_f\)) |
2 GPa |
Biot coefficient (\(\alpha\)) |
1.0 |
porosity (\(n\)) |
0.4 |
permeability (\(k\)) |
2.98 × 10-8 \({m^2}/{Pa-sec}\) |
The initial pore pressure is 147 kPa, and the initial isotropic stress is -147 kPa. Because the Biot coefficient is equal to one (incompressible soil grains), the Biot modulus is equal to the ratio between water bulk modulus and porosity (in this case, \(M\) = 5 GPa). The well-pumping rate per unit aquifer thickness is 2.21 10-3 m2/s, and the well radius, \(r_w\), is selected as 1 m.
Stresses and pore pressures are initialized to the values given above. The well flow-rate is modeled as a surface flux of magnitude \(q/(2 \pi r_w)\) applied to the well radius \(r = r_w\).
The coupled problem is solved using the model solve-fluid-coupled command with the implicit servo. The mechanical convergence is limited to 1.0.
This example is pore-pressure driven, and the value for the stiffness ratio, \(R_k\), is
approximately 23 for the specified fluid bulk modulus of 2 GPa. Thus, the flow calculation may be
uncoupled from the mechanical calculation, and the approach discussed in Stiffness Ratio may be
applied. The fluid modulus during the flow-only step is scaled using zone fluid modulus-scaled in order to preserve the diffusivity of the system.
The zone fluid solve-fluid-decoupled command is used in 8 stages for a total of 32 seconds.
Note that, if conditions are such that \(R_k <<< 1\), it is not necessary to adjust the fluid modulus during the flow calculation because the diffusivity will be accurate.
The analytical solutions for pore pressure, stresses, and vertical displacement are programmed as a FISH function. The exponential integral function used in the analytical solutions is programmed as a separate FISH function. Analytical and numerical values are stored in tables. The results are then compared in graphical form. The pore-pressure comparison at selected times is presented in Figure 3 for the coupled solution, and Figure 4 for the uncoupled solution. The vertical displacement values and stresses at 32 seconds are processed by the FISH function well_32 and are illustrated in Figure 5 and Figure 7 for the coupled solution, and in Figure 6 and Figure 8 for the uncoupled solution.
The results for both the coupled and uncoupled solutions are essentially identical and compare well with the analytical solution. The uncoupled solution is reached much more quickly than the coupled solution. Note that the coupled calculation requires more than 120,000 steps, while the uncoupled calculation requires approximately 4,200 steps.
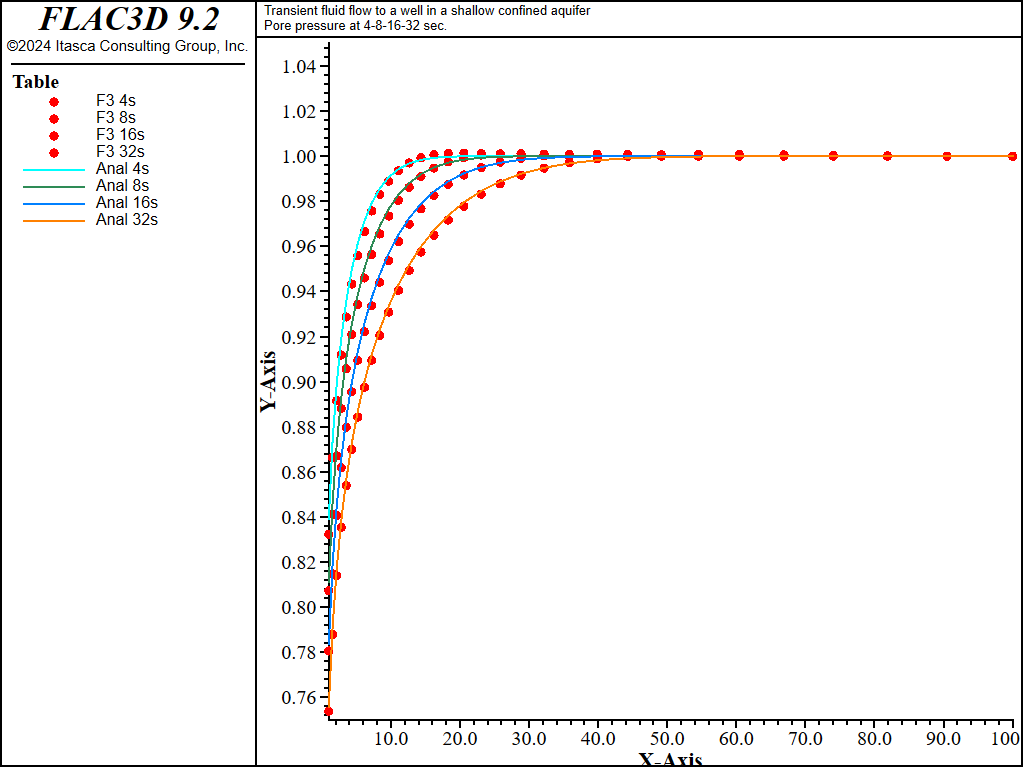
Figure 3: Pore-pressure distribution at 4, 8, 16, and 32 seconds—coupled solution (analytical values = lines; numerical values = symbols).
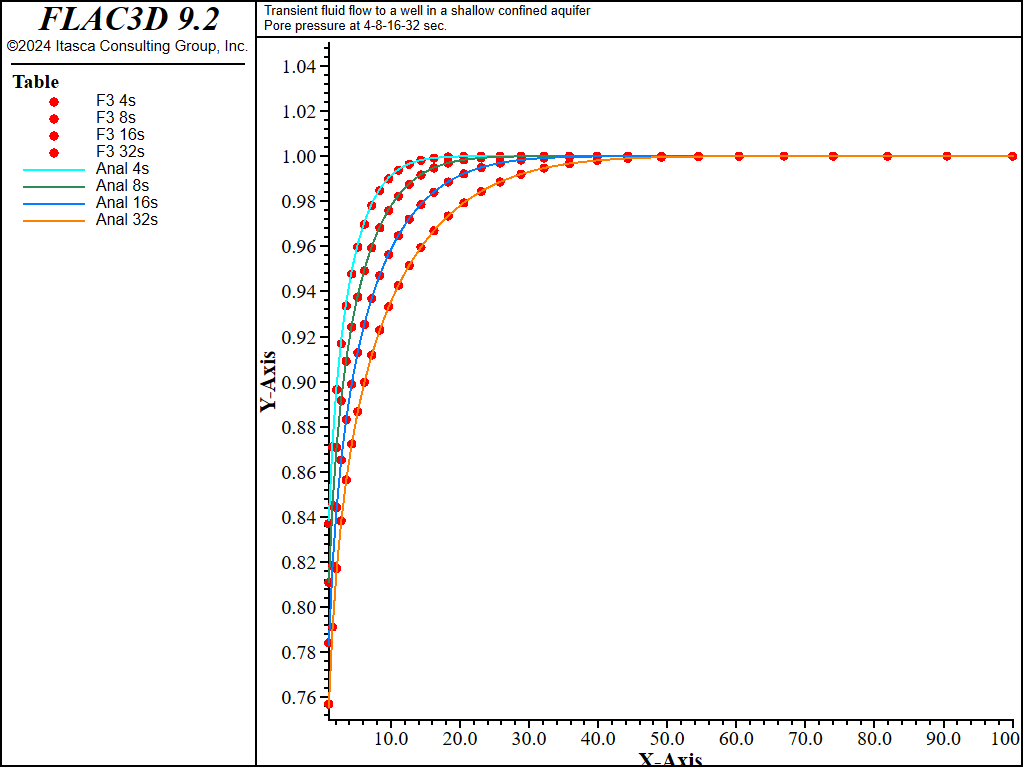
Figure 4: Pore-pressure distribution at 4, 8, 16, and 32 seconds—uncoupled solution (analytical values = lines; numerical values = symbols).
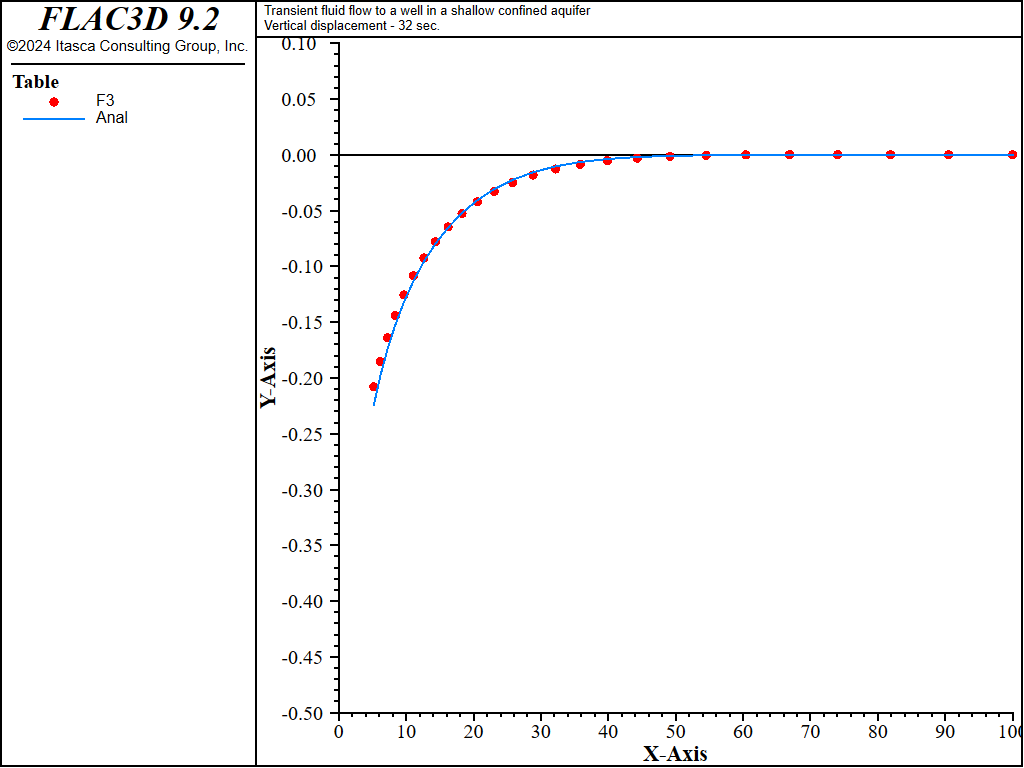
Figure 5: Radial, tangential, and vertical stress distributions at 32 seconds — coupled solution (analytical values = lines; numerical values = symbols).
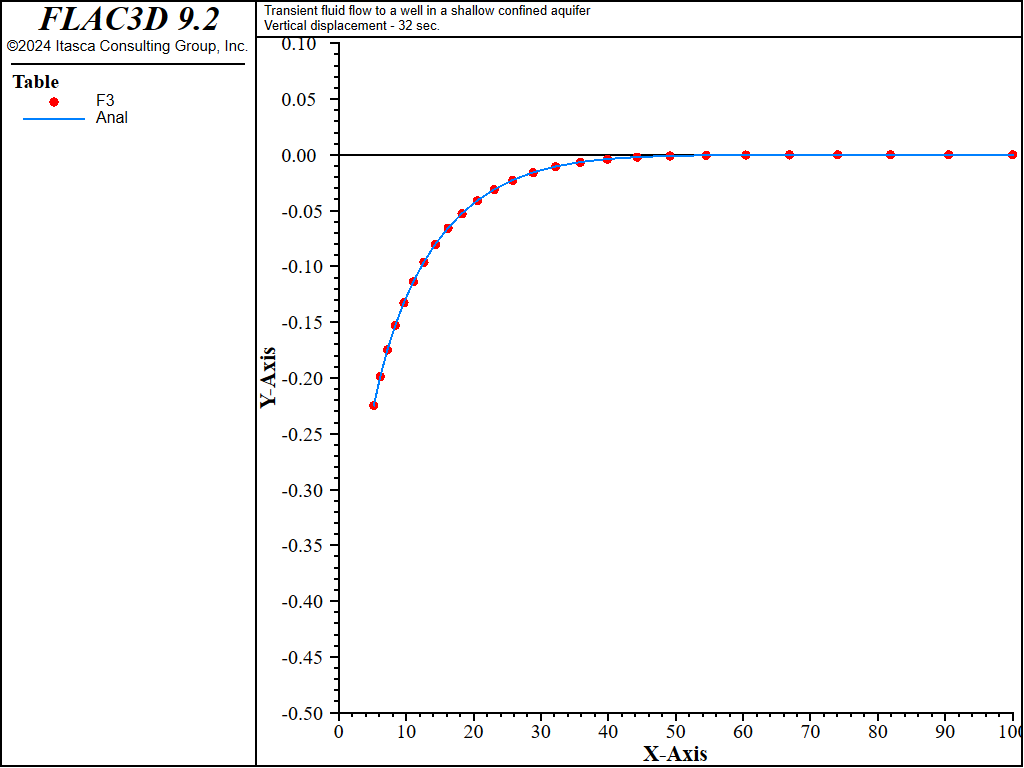
Figure 6: Radial, tangential, and vertical stress distributions at 32 seconds — uncoupled solution (analytical values = lines; numerical values = symbols).
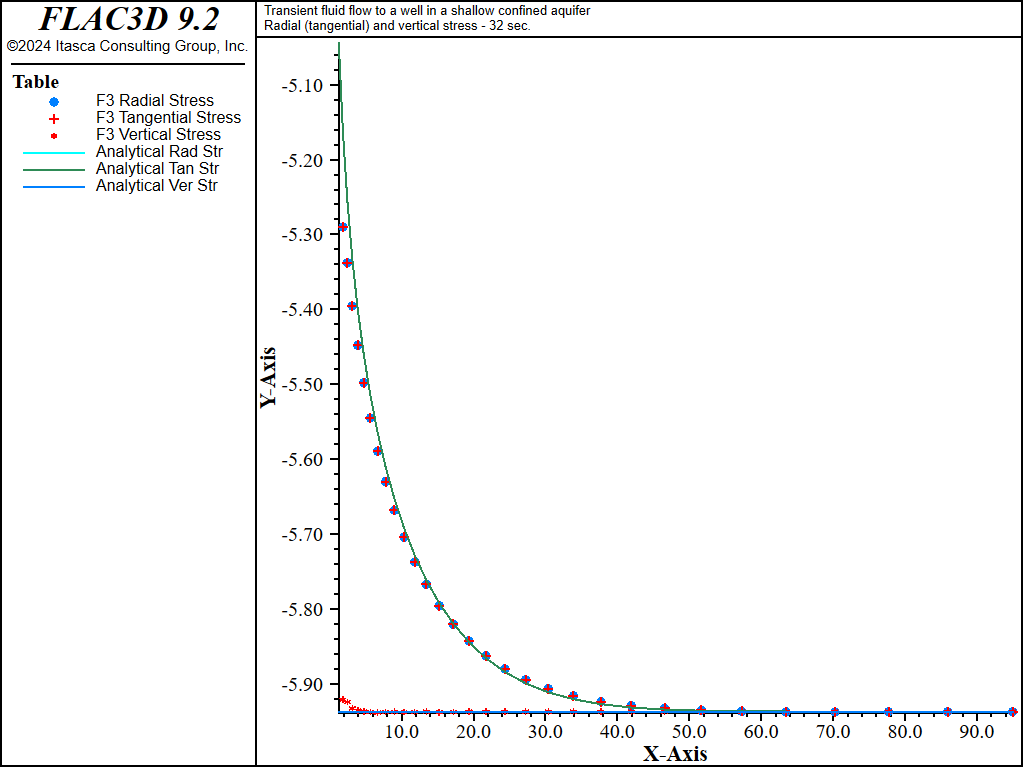
Figure 7: Radial displacement distribution at 32 seconds—coupled solution (analytical values = line; numerical values = symbols).
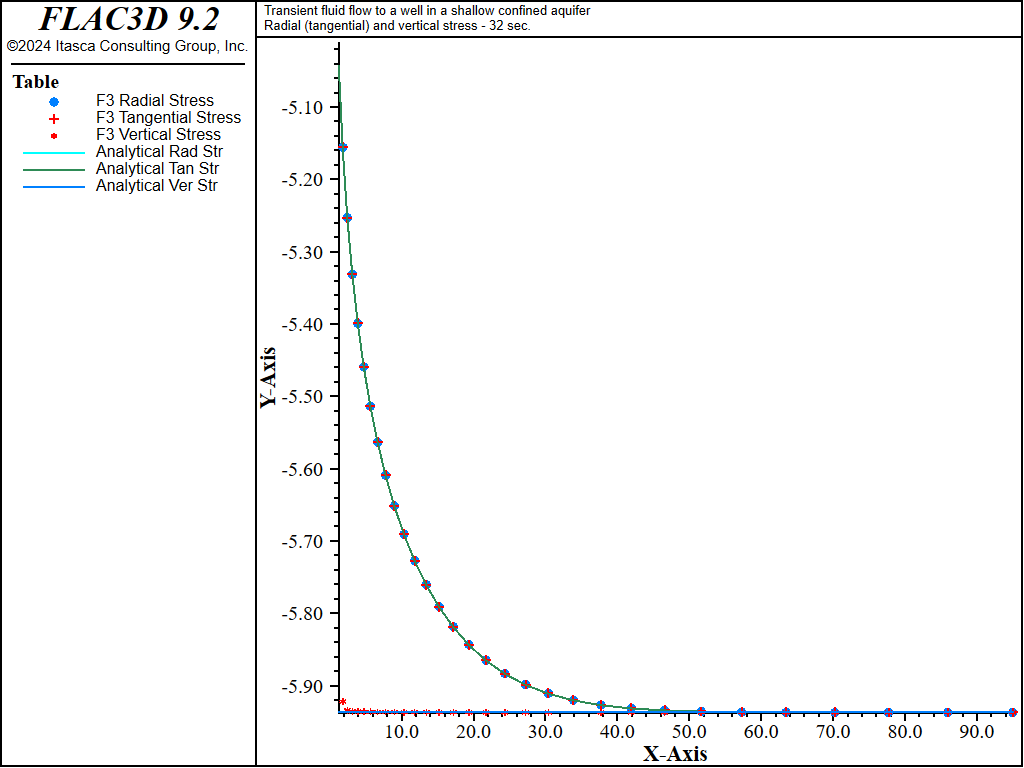
Figure 8: Radial displacement distribution at 32 seconds—uncoupled solution (analytical values = line; numerical values = symbols).
Reference
Theis, C. V. “The Relation between the Lowering of the Piezometric Surface and the Rate and Duration of Discharge of a Well Using Groundwater Storage,” Trans. Am. Geophys. Union, 10, 519-524 (1935).
Data File
WellConfinedAquifer.dat
model new
model title 'Transient fluid flow to a well in a shallow confined aquifer'
; --- model geometry (hollow cylinder - 9 degree wedge) ---
zone create brick point 0 (1,0,0) point 1 (100,0,0) ...
point 2 (0.987688,0.156434,0) point 3 (1,0,1) ...
point 4 (98.7688,15.6434,0) point 5 (0.987688,0.156434,1) ...
point 6 (100,0,1) point 7 (98.7688,15.6434,1) ...
size (31,1,1) ratio (1.1,1,1)
zone face skin
; --- mechanical model ---
zone cmodel assign elastic
zone property bulk 11.8e7 shear 7.1e7
zone face apply velocity-x 0
zone face apply velocity-y 0
zone face apply velocity-z 0 range group 'Bottom'
zone initialize stress xx -1.47e5 yy -1.47e5 zz -1.47e5
zone face apply stress-normal -1.47e5 range group 'Top'
; --- fluid flow model ---
model configure fluid-flow
zone fluid property mobility-coefficient 2.98e-8 porosity 0.4 ...
fluid-modulus 2e9
zone gridpoint pore-pressure initialize 147000
; [] = Equivalent flux
zone face apply discharge [-2.21e-3/(2*math.pi)] range group 'West'
; --- setting ---
model large-strain off
model save 'well-ini'
; --- pumping (coupled analysis) ---
zone fluid property pore-pressure-generation on
zone fluid implicit servo on
model solve-fluid-coupled time 4 convergence 1
model save 'well-cpl4'
model solve-fluid-coupled time 4 convergence 1
model save 'well-cpl8'
model solve-fluid-coupled time 8 convergence 1
model save 'well-cpl16'
model solve-fluid-coupled time 16 convergence 1
model save 'well-cpl32'
;
; --- pumping (uncoupled analysis) ---
model restore 'well-ini'
zone fluid modulus-scale ; Adjusted fluid modulus
zone fluid implicit servo on
model solve-fluid-decoupled time 32 stages 8 convergence 1 ...
stage-save 'well-ucpl'
| Was this helpful? ... | Itasca Software © 2024, Itasca | Updated: Dec 05, 2024 |
