Examples • Example Applications
Undrained Cylindrical Cavity Expansion in a Cam-Clay Medium (FLAC2D)
Problem Statement
Note
The project file for this example is available to be viewed/run in FLAC2D.[1] The project’s main data file is shown at the end of this example.
The stress and pore-pressure changes due to the expansion of a pressuremeter in a saturated clay mass are analyzed using the model of a cylindrical cavity in an infinite (in the out-of-plane direction) Cam-clay medium. The effect of the finite length of the measuring device is not considered.
In the experiment, the radius \(a\) of the cavity is expanded up to twice its original size, \(a_0\). The properties of the Cam-clay material, which correspond to a Boston Blue Clay, are as follows (Carter et al., 1979):
undrained cohesion (\(C_u\)) |
1 MPa |
shear modulus (\(G\)) |
74 × \(C_u\) |
soil constant (\(M\)) |
1.2 |
slope of normal consolidation line (λ) |
0.15 |
slope of elastic swelling line (κ) |
0.03 |
reference pressure (\(p_1\)) |
\(C_u\) |
specific volume at reference pressure (\(v_λ\)) |
2.3 |
The clay is normally consolidated with in-situ stresses \(σ'_r\) = \(σ'_θ\) = -1.65 \(C_u\), \(σ'_z\) = -3 \(C_u\) and initial excess pore pressure \(u_e\) = 0. The shear modulus of the material is assumed to remain constant during the simulation. The pressuremeter membrane is considered impermeable, and the fluid bulk modulus is much larger than that of the soil so that the numerical simulation can be carried out under undrained conditions.
FLAC2D Model
The FLAC2D model is constructed by taking into consideration the axisymmetric and plane-strain properties of the problem. A pie slice corresponding to one-tenth of a quadrant and of height \(h\) is considered (see the front view in Figure 1). The FLAC2D model is of finite extent, but the length \(L\) is chosen as very large compared to \(a_0\).
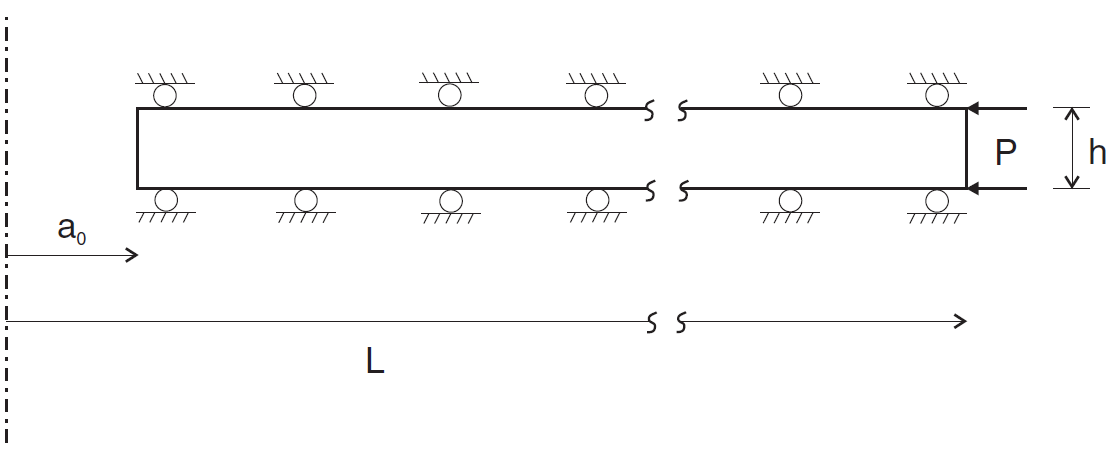
Figure 1: Front view of the model geometry.
The dimensions of the FLAC2D grid correspond to dimensionless values \(a_0 \big/ a_0\) = 1, \(L \big/ a_0\) = 200 and \(h \big/ a_0\) = 1. The grid is composed of 31 zones of variable zone width, graded by a factor 1.1 (see Figure 2). The image also represents applied boundary conditions.
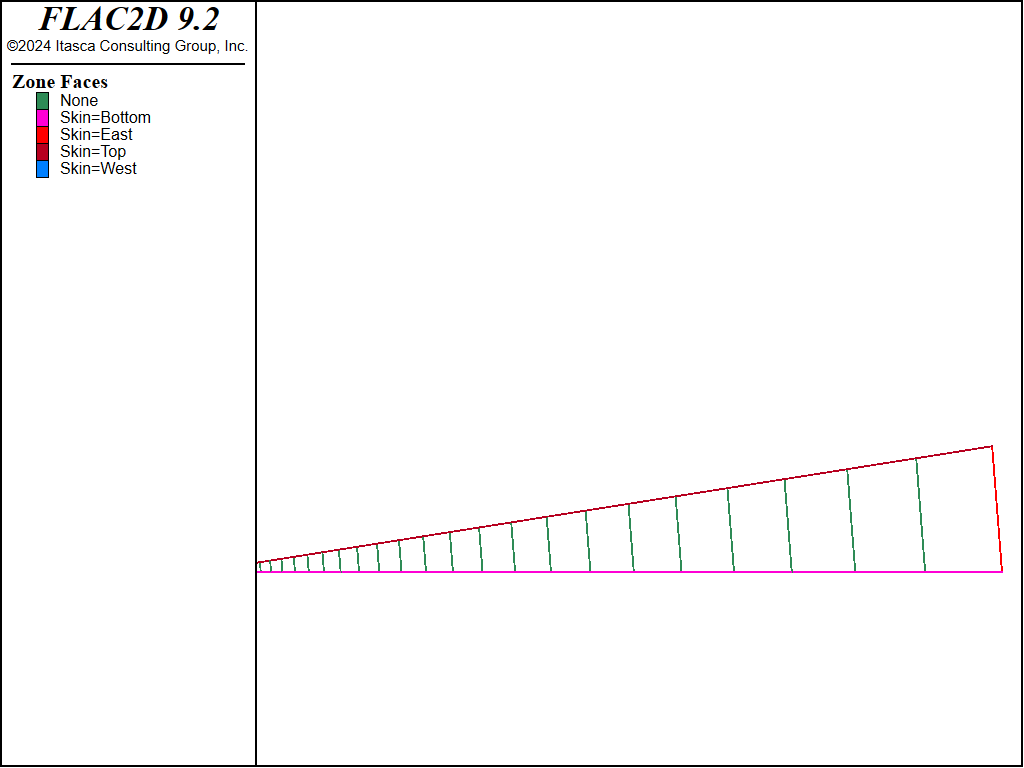
Figure 2: Grid geometry and applied boundary conditions.
Initially, the cavity boundary is fixed, in-situ stresses are installed, and a pressure boundary condition of magnitude 1.65 \(C_u\) is applied at the far \(x\)-boundary. The groundwater configuration (model configure fluid-flow) is selected, and the no-flow (model fluid active off) and large-strain (model large-strain on) options are specified.
The pre-consolidation pressure must be supplied to the numerical model. Since the soil is normally consolidated, this value is calculated from the given initial state. The corresponding values of mean pressure and deviator stress are \(p'_0\) = 2.1 \(C_u\) and \(q_0\) = 1.35 \(C_u\), and the pre-consolidation pressure, evaluated from the Cam-clay yield function (see <section 1 in Constitutive Models>), preceding link waiting to be built for final location of CModel material
is 2.70 \(C_u\). For information, the value of the over-consolidation ratio \(R\), defined as \(R\) = \(p^{\prime}_{c0}\)/\(p'_0\), is approximately 1.29 for this problem.
As an illustration, initial values for the specific volume, \(v_0\) , and tangent bulk modulus, \(K_0\) , are specified. They correspond to the default values that would have been assigned by the code at the first step command.
By default, the Biot coefficient is equal to one. The Biot modulus (water bulk modulus divided by porosity) is set to 100 times \(K_0\). The maximum bulk modulus is set to 10 times the initial value.
A compressive velocity of magnitude 10-5 is applied at the cavity boundary for a total of 100,000 steps, so that the cavity radius has doubled at the end of the pressure test. Stresses and pore pressure are monitored during the calculation.
The data file for this problem is listed at the end of this section. The Cam-clay parameters are calculated in the FISH function setProp.
FLAC2D Results and Discussion
The evolution during the expansion of the deviator stress, \(q \big/ C_u\), at the cavity wall is plotted in Figure 3. The numerical results indicate a failure level at \(q \big/ C_u\) = 1.779. This value can be compared to the Cam-clay analytical prediction as follows. Under undrained conditions, the yield path followed by a normally consolidated stress point has the form (see the verification problem Drained and Undrained Triaxial Compression Test on a Cam-Clay Sample),
where \(\eta = q\big/p'\) and \(\Lambda = (\lambda-\kappa)\big/\lambda\). The initial value \(\eta_0 = q_0\big/p'_0\) can be derived from equation (1) above. Using the definition of \(R\), we obtain
and the stress path becomes
Intersection of this stress path with the critical state line \(q = M p'\) or \(\eta = M\) gives
The prediction of \(q_{cr}\big/C_u\) derived from this formula is 1.771, which is in close agreement with that obtained numerically.
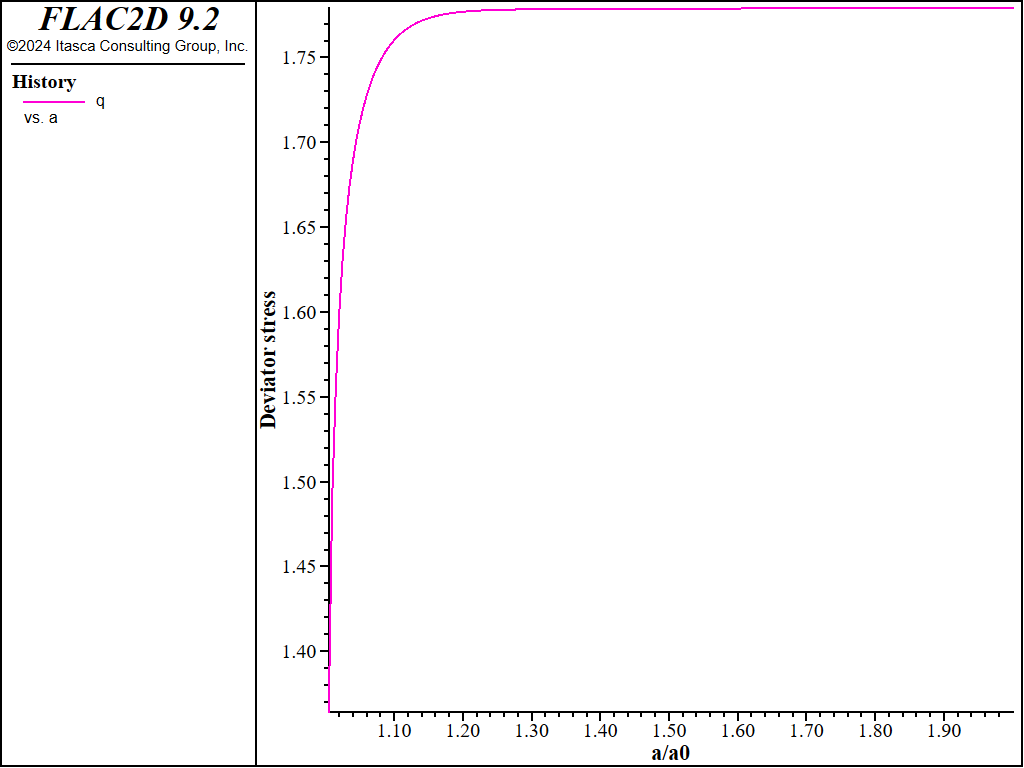
Figure 3: Deviator stress \(q\)/\(C_u\) at the cavity wall versus \(a\)/\(a_0\).
The variation of excess pore pressure and total radial stress at the cavity wall as the cavity expands is illustrated in Figure 4. These curves show a sharp rise followed by a gentle slope as pore pressure and radial stress approach a limit value.
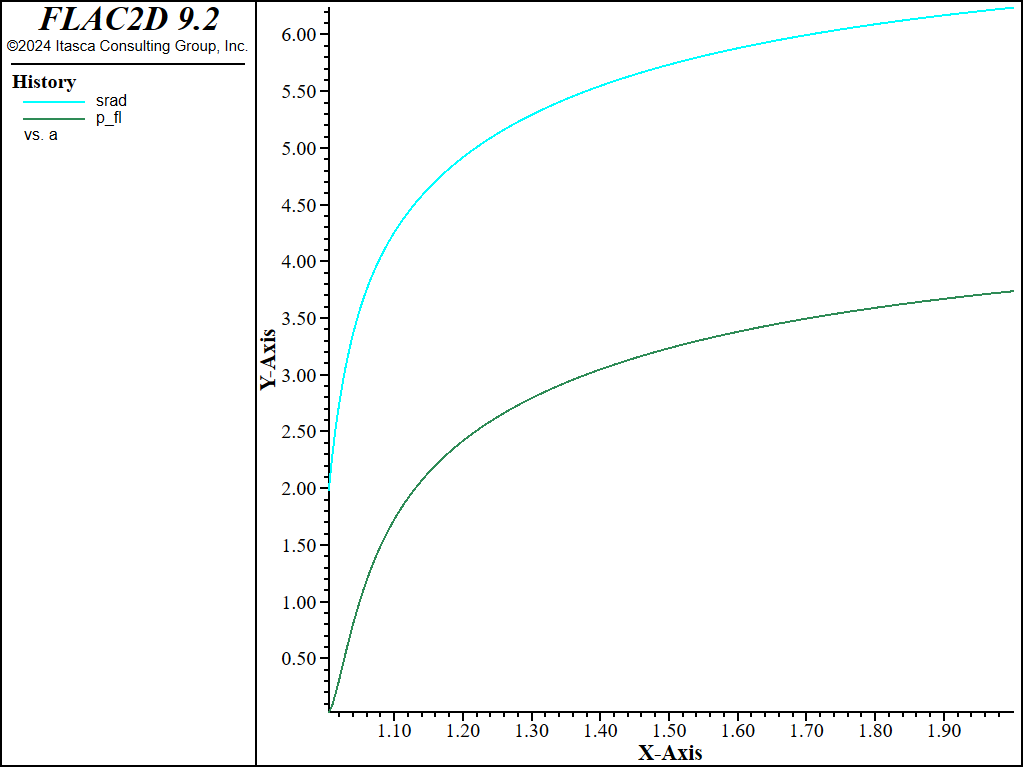
Figure 4: Total radial stress \(σ_r\)/\(C_u\) and excess pore pressure \(u_e\)/\(C_u\) at the cavity wall versus \(a\)/\(a_0\).
The radial distribution of effective stresses and pore pressure when \(a = 2a_0\) is plotted in Figure 5. The stresses remain constant in an annulus around the cavity where the soil is at the critical state. There, the distribution of stresses has been greatly affected by the process of cavity expansion, with radial and tangential stresses now in the role of minor and major principal stresses. The excess pore pressure develops mainly in this region. Farther out, the stresses and pore pressure are shown to evolve towards their in-situ values. These results compare well with those presented by Carter et al. (1979).
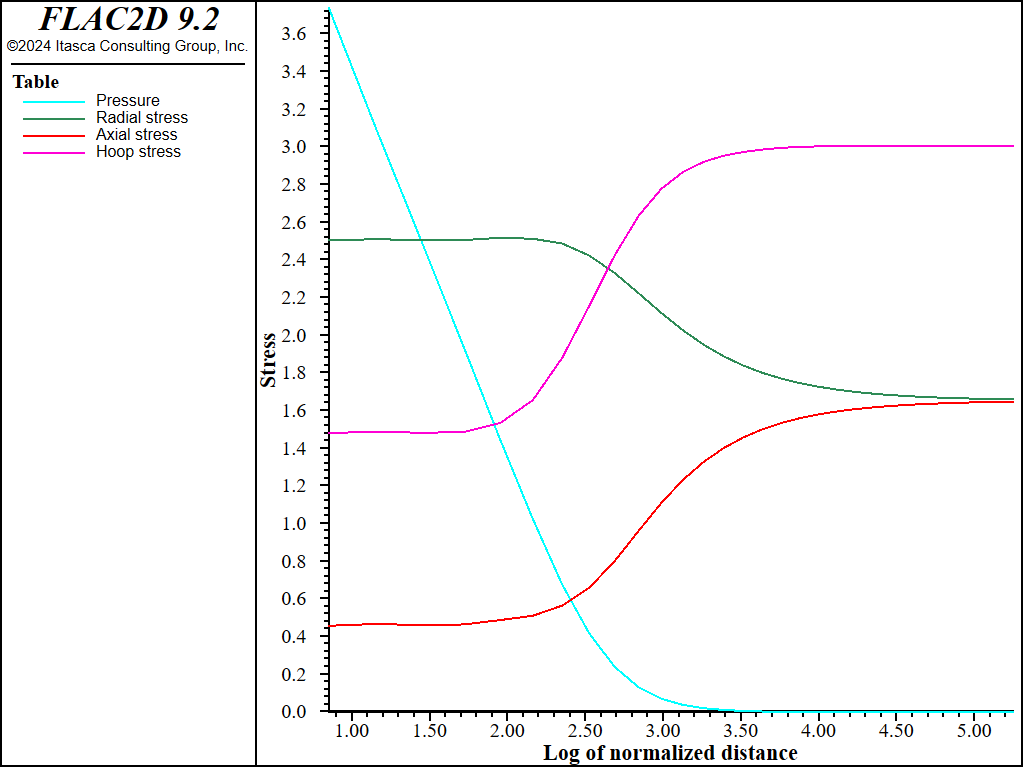
Figure 5: Radial distribution of effective stresses and pore pressure when \(a\) = 2 \(a_0\) plotted versus \(ln\) ( \(r\)/\(a_0\) ).
Reference
Carter, J. P., M. F. Randolph and C. P. Wroth. “Stress and Pore Pressure Changes in Clay during and after the Expansion of a Cylindrical Cavity,” International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 3, 305-322 (1979).
Data File
CavityExpansion.dat
;-----------------------------------------------------------
; Undrained cylindrical cavity expansion in Cam-Clay medium
;-----------------------------------------------------------
model new
model title "Undrained cylindrical cavity expansion in Cam-Clay medium"
; --- model geometry ---
zone create2d quadrilateral point 0 1.0 0.0 ...
point 1 200.0 0.0 ...
point 2 0.9877 0.1564 ...
point 3 197.5377 31.2869 ...
size 31 1 ratio 1.1 1
zone face skin ; Name model boundaries
; --- mechanical
model large-strain on
zone cmodel assign modified-cam-clay
zone property shear 74.
zone property ratio-critical-state 1.2 lambda 0.15 kappa 0.03 ...
pressure-reference 1.0 specific-volume-reference 2.3
zone initialize stress xx -1.65 yy -1.65 zz -3.
program call 'utility' suppress ; FISH functions used by the example
[effectivePressure] ; Initializes pressure-effective property
; --- boundary conditions ---
zone face apply stress-normal -1.65 range group 'East'
zone face apply velocity-normal 0 range group 'Top' or 'Bottom'
zone gridpoint fix velocity range group 'West'
zone gridpoint initialize velocity-x 1e-5 range group 'West'
; --- fluid
model configure fluid-flow
zone fluid property pore-pressure-generation on
; --- histories ---
history interval 500
fish history name='srad' srad
fish history name='p_fl' p_fl
fish history name='a' a
fish history name='q' q
; --- test ---
[setProp] ; Initializes biot mod, pressure-preconsolidation, and bulk-maximum
model solve-static cycles-total 100000
model save 'cavity'
Endnote
| Was this helpful? ... | Itasca Software © 2024, Itasca | Updated: Dec 05, 2024 |
